Our Previous Samples
The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Example 1The Concept of a Knowled ...
The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Example 1
The Concept of a Knowledge Worker
- Employs intellect to analyze, create, and share valuable information.
- Utilizes expertise to solve complex problems and make informed decisions.
- Relies on continuous learning and innovation for professional growth.
- Leverages technology to access, organize, and disseminate knowledge effectively.
- Collaborates with multidisciplinary teams to improve patient outcomes and care.
- Drives evidence-based practices and fosters a culture of lifelong learning.
(Garcia-Dia, 2021)
Nursing Informatics – Definition and Explanation
- Integration of nursing science, computer science, and information science.
- Enhances healthcare through data management, knowledge dissemination, and technology.
- Improves patient care, safety, and outcomes through evidence-based practice.
- Utilizes technology to collect, analyze, and interpret healthcare data.
- Supports decision-making, research, and quality improvement in nursing practice.
- Optimizes information systems to streamline workflows and enhance communication
- (Kianto et al., 2019)
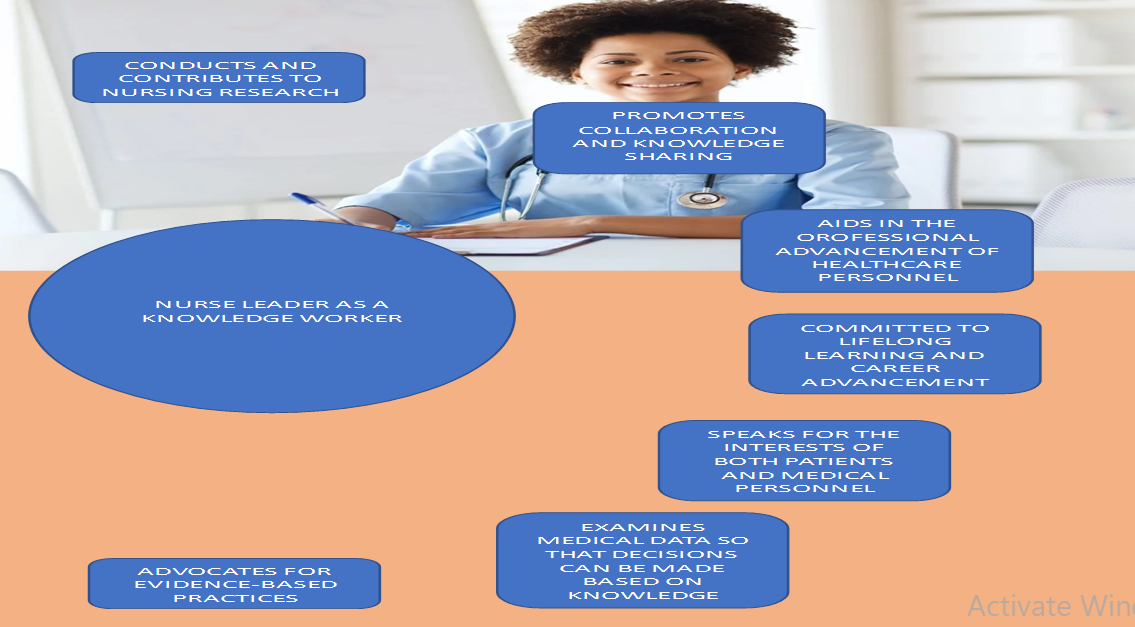
Nurse Leader as a Knowledge Worker
- Strategically integrates evidence-based practices into nursing leadership.
- Promotes continuous learning and professional development among the team.
- Facilitates knowledge sharing and collaboration across healthcare disciplines.
- Utilizes data and technology to drive informed decision-making and innovation.
- Advocates for a culture of lifelong learning and evidence-based care.
- Inspires and empowers the team to embrace knowledge-driven practices.
- (Strudwick et al., 2019)
The Application of Data to Problem-Solving in Healthcare
- Examining data: Vital signs, glucose levels, physical activity, sleep patterns.
- Data collection: Wearable devices, sensors, secure transmission to a centralized database.
- Derived knowledge: Early identification, personalized treatment, proactive preventive care.
- Accessing data: Secure web portal, a mobile application for real-time monitoring.
- Clinical reasoning: Nurse leaders interpret data, consider patient context.
- Improving outcomes: Data-driven insights, evidence-based practice, process improvement.
The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 References
Garcia-Dia, M. J. (2021). Nursing informatics: an evolving specialty. Nursing Management, 52(5), 56. https://journals.lww.com/nursingmanagement/fulltext/2021/05000/nursing_informatics__an_evolving_specialty.10.aspx
Kianto, A., Shujahat, M., Hussain, S., Nawaz, F., & Ali, M. (2019). The impact of knowledge management on knowledge worker productivity. Baltic Journal of Management, 14(2), 178-197. https://hub.hku.hk/bitstream/10722/278661/1/Content.pdf?accept=1
Strudwick, G., Nagle, L., Kassam, I., Pahwa, M., & Sequeira, L. (2019). Informatics Competencies for Nurse Leaders: A Scoping Review. The Journal of Nursing Administration, 49(6), 323–330. https://doi.org/10.1097/NNA.0000000000000760
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 / NURS 5051 Instructions
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker
The term “knowledge worker” was first coined by management consultant and author Peter Drucker in his book, The Landmarks of Tomorrow (1959). Drucker defined knowledge workers as high-level workers who apply theoretical and analytical knowledge, acquired through formal training, to develop products and services. Does this sound familiar?
Nurses are very much knowledge workers. What has changed since Drucker’s time are the ways that knowledge can be acquired. The volume of data that can now be generated and the tools used to access this data have evolved significantly in recent years and helped healthcare professionals (among many others) to assume the role of knowledge worker in new and powerful ways.
In this Assignment, you will consider the evolving role of the nurse leader and how this evolution has led nurse leaders to assume the role of knowledge worker. You will prepare a PowerPoint presentation with an infographic (graphic that visually represents information, data, or knowledge. Infographics are intended to present information quickly and clearly.) to educate others on the role of nurse as knowledge worker.
Reference: Drucker, P. (1959). The landmarks of tomorrow. New York, NY: HarperCollins Publishers.
To Prepare for this The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051:
- Review the concepts of informatics as presented in the Resources.
- Reflect on the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker.
- Consider how knowledge may be informed by data that is collected/accessed.
The Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051:
- Explain the concept of a knowledge worker.
- Define and explain nursing informatics and highlight the role of a nurse leader as a knowledge worker.
- Include one slide that visually represents the role of a nurse leader as knowledge worker.
- Your PowerPoint should Include the hypothetical scenario you originally shared in the Discussion Forum. Include your examination of the data that you could use, how the data might be accessed/collected, and what knowledge might be derived from that data. Be sure to incorporate feedback received from your colleagues’ responses.
By Day 7 of Week 2
Submit your completed Presentation.
Assignment: The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Example 2 Presentation
The Knowledge Worker
- Knowledge workers are people who use their theoretical knowledge and acquired skills through formal training to deliver productive work (Druker, 1995).
- Knowledge workers use their knowledge and skills to solve complex problems, make decisions, and provide new services.
- Knowledge workers access and synthesize information and use analytic reasoning and relevant judgments in addressing issues and new situations.
- Good communication skills and adequate motivation help knowledge workers deliver quality service.
- A professional board always governs knowledge workers
- Knowledge workers receive higher compensation due to the complex nature of their work
Nursing Informatics
- Nursing informatics combines nursing science, information science, and computer science (McGonigle & Mastrian, 2015.)
- This combination helps identify, define, manage, and communicate information, wisdom, and data in nursing practice to improve patient care.
- Nursing informatics includes bed management systems that help manage patient census and an electronic portal that allows patients to access their medical records quickly.
- Radio frequency identification is another example of nursing informatics that aids in tracking patient and caregiver activities.
- Nursing informatics is essential in increasing patient safety and promoting quality healthcare in hospital settings.
- Nursing informatics plays a vital role in training nursing staff on the use of technology, answering questions, and monitoring results.
Nursing informatics improve patient care by:
- Designing different process of treatment approaches, reviewing clinical workflow, diagnostic and treatment plans
- Measuring and analyzing different parts of organizational roles and making specific changes that help in improving patient care.
- Analyzing several data information to identify prevalent issues in healthcare organizations and provide the best solutions
- Selecting and testing new medical devices used in improving patient care.
- Providing training to other nursing staff by providing educational programs.
- Implementing information systems provides better access to evidence affecting patient safety and supports evidence-based nursing.
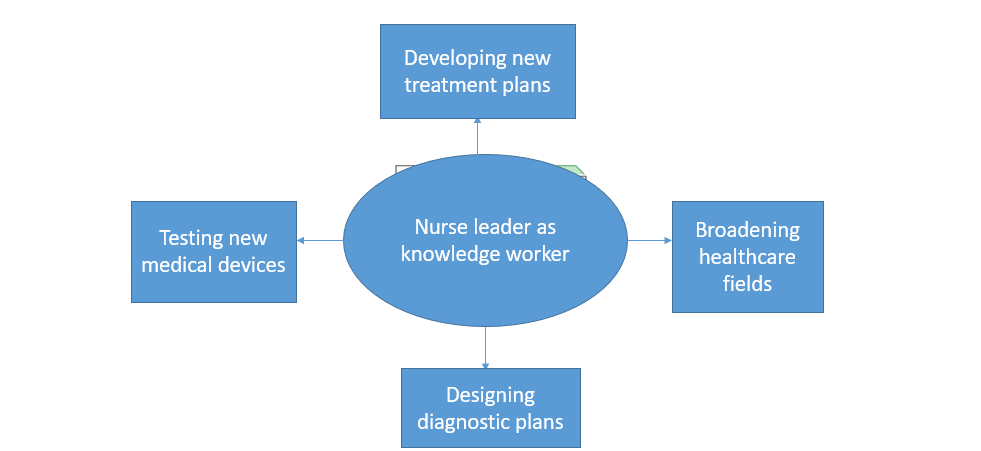
Role of a Nurse as a Knowledge Worker
- Nurse leaders play a crucial work in developing new treatment plans, collecting and evaluating treatment plans
- Using their autonomy and nursing experience, nursing leaders aid in broadening healthcare fields and promoting health
- Nurse leaders apply their knowledge and skills to address the needs of their patients and level up the general patient care criteria.
- Nurse leaders use their acquired integrated knowledge to solve upcoming and existing practice problems in healthcare settings.
- Nurse leaders are equipped with informatics skills that aid in developing new research on different nursing practices that help in improving outcomes of patient needs.
The Nurse Leader as Knowledge Worker NURS 6051 Presentation References
- Drucker, P. (1959). Landmarks of Tomorrow: A Report on the New” Post-Modern. World.
- McGonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (Eds.). (2015). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge. Jones & Bartlett Publishers
NURS 6051 Week 3 Discussion: Interaction Between Nurse Informaticists and Other Specialists
Nature offers many examples of specialization and collaboration. Ant colonies and bee hives are but two examples of nature’s sophisticated organizations. Each thrives because their members specialize by tasks, divide labor, and collaborate to ensure food, safety, and general well-being of the colony or hive.
Of course, humans don’t fare too badly in this regard either. And healthcare is a great example. As specialists in the collection, access, and application of data, nurse informaticists collaborate with specialists on a regular basis to ensure that appropriate data is available to make decisions and take actions to ensure the general well-being of patients.
In this Discussion, you will reflect on your own observations of and/or experiences with informaticist collaboration. You will also propose strategies for how these collaborative experiences might be improved.
To Prepare:
- Review the Resources and reflect on the evolution of nursing informatics from a science to a nursing specialty.
- Consider your experiences with nurse Informaticists or technology specialists within your healthcare organization.
By Day 3 of Week 3
Post a description of experiences or observations about how nurse informaticists and/or data or technology specialists interact with other professionals within your healthcare organization. Suggest at least one strategy on how these interactions might be improved. Be specific and provide examples. Then, explain the impact you believe the continued evolution of nursing informatics as a specialty and/or the continued emergence of new technologies might have on professional interactions.
By Day 6 of Week 3
Respond to at least two of your colleagues* on two different days, offering one or more additional interaction strategies in support of the examples/observations shared or by offering further insight to the thoughts shared about the future of these interactions.
*Note: Throughout this program, your fellow students are referred to as colleagues.
NURS 6051 Week 3 Assignment: The Impact of Nursing Informatics on Patient Outcomes and Patient Care Efficiencies
In the Discussion for this module, you considered the interaction of nurse informaticists with other specialists to ensure successful care. How is that success determined?
Patient outcomes and the fulfillment of care goals is one of the major ways that healthcare success is measured. Measuring patient outcomes results in the generation of data that can be used to improve results. Nursing informatics can have a significant part in this process and can help to improve outcomes by improving processes, identifying at-risk patients, and enhancing efficiency.
To Prepare:
- Review the concepts of technology application as presented in the Resources.
- Reflect on how emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence may help fortify nursing informatics as a specialty by leading to increased impact on patient outcomes or patient care efficiencies.
The Assignment: (4-5 pages not including the title and reference page)
In a 4- to 5-page project proposal written to the leadership of your healthcare organization, propose a nursing informatics project for your organization that you advocate to improve patient outcomes or patient-care efficiency. Your project proposal should include the following:
- Describe the project you propose.
- Identify the stakeholders impacted by this project.
- Explain the patient outcome(s) or patient-care efficiencies this project is aimed at improving and explain how this improvement would occur. Be specific and provide examples.
- Identify the technologies required to implement this project and explain why.
- Identify the project team (by roles) and explain how you would incorporate the nurse informaticist in the project team.
- Use APA format and include a title page and reference page.
- Use the Safe Assign Drafts to check your match percentage before submitting your work.
By Day 7 of Week 4
Submit your completed Project Proposal.
NURS 6051 Week 5 Discussion: Big Data Risks and Rewards
When you wake in the morning, you may reach for your cell phone to reply to a few text or email messages that you missed overnight. On your drive to work, you may stop to refuel your car. Upon your arrival, you might swipe a key card at the door to gain entrance to the facility. And before finally reaching your workstation, you may stop by the cafeteria to purchase a coffee.
From the moment you wake, you are in fact a data-generation machine. Each use of your phone, every transaction you make using a debit or credit card, even your entrance to your place of work, creates data. It begs the question: How much data do you generate each day? Many studies have been conducted on this, and the numbers are staggering: Estimates suggest that nearly 1 million bytes of data are generated every second for every person on earth.
As the volume of data increases, information professionals have looked for ways to use big data—large, complex sets of data that require specialized approaches to use effectively. Big data has the potential for significant rewards—and significant risks—to healthcare. In this Discussion, you will consider these risks and rewards.
To Prepare:
- Review the Resources and reflect on the web article Big Data Means Big Potential, Challenges for Nurse Execs.
- Reflect on your own experience with complex health information access and management and consider potential challenges and risks you may have experienced or observed.
By Day 3 of Week 5
Post a description of at least one potential benefit of using big data as part of a clinical system and explain why. Then, describe at least one potential challenge or risk of using big data as part of a clinical system and explain why. Propose at least one strategy you have experienced, observed, or researched that may effectively mitigate the challenges or risks of using big data you described. Be specific and provide examples.
By Day 6 of Week 5
Respond to at least two of your colleagues* on two different days, by offering one or more additional mitigation strategies or further insight into your colleagues’ assessment of big data opportunities and risks.
*Note: Throughout this program, your fellow students are referred to as colleagues.
Submission and Grading Information
Week 6 Discussion: Healthcare Information Technology Trends
Throughout history, technological advancements have appeared for one purpose before finding applications elsewhere that lead to spikes in its usage and development. The internet, for example, was originally developed to share research before becoming a staple of work and entertainment. But technology—new and repurposed—will undoubtedly continue to be a driver of healthcare information. Informaticists often stay tuned to trends to monitor what the next new technology will be or how the next new idea for applying existing technology can benefit outcomes.
In this Discussion, you will reflect on your healthcare organization’s use of technology and offer a technology trend you observe in your environment.
To Prepare:
- Reflect on the Resources related to digital information tools and technologies.
- Consider your healthcare organization’s use of healthcare technologies to manage and distribute information.
- Reflect on current and potential future trends, such as use of social media and mobile applications/telehealth, Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled asset tracking, or expert systems/artificial intelligence, and how they may impact nursing practice and healthcare delivery.
By Day 3 of Week 6
Post a brief description of general healthcare technology trends, particularly related to data/information you have observed in use in your healthcare organization or nursing practice. Describe any potential challenges or risks that may be inherent in the technologies associated with these trends you described. Then, describe at least one potential benefit and one potential risk associated with data safety, legislation, and patient care for the technologies you described. Next, explain which healthcare technology trends you believe are most promising for impacting healthcare technology in nursing practice and explain why. Describe whether this promise will contribute to improvements in patient care outcomes, efficiencies, or data management. Be specific and provide examples.
By Day 6 of Week 6
Respond to at least two of your colleagues* on two different days, offering additional/alternative ideas regarding opportunities and risks related to the observations shared.
*Note: Throughout this program, your fellow students are referred to as colleagues.
Week 6 Assignment: Literature Review: The Use of Clinical Systems to Improve Outcomes and Efficiencies
New technology—and the application of existing technology—only appears in healthcare settings after careful and significant research. The stakes are high, and new clinical systems need to offer evidence of positive impact on outcomes or efficiencies.
Nurse informaticists and healthcare leaders formulate clinical system strategies. As these strategies are often based on technology trends, informaticists and others have then benefited from consulting existing research to inform their thinking.
In this Assignment, you will review existing research focused on the application of clinical systems. After reviewing, you will summarize your findings.
To Prepare:
- Review the Resources and reflect on the impact of clinical systems on outcomes and efficiencies within the context of nursing practice and healthcare delivery.
- Conduct a search for recent (within the last 5 years) research focused on the application of clinical systems. The research should provide evidence to support the use of one type of clinical system to improve outcomes and/or efficiencies, such as “the use of personal health records or portals to support patients newly diagnosed with diabetes.”
- Identify and select 4 peer-reviewed research articles from your research.
- For information about annotated bibliographies, visit https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/assignments/annotatedbibliographies
The Assignment: (4-5 pages not including the title and reference page)
In a 4- to 5-page paper, synthesize the peer-reviewed research you reviewed. Format your Assignment as an Annotated Bibliography. Be sure to address the following:
- Identify the 4 peer-reviewed research articles you reviewed, citing each in APA format.
- Include an introduction explaining the purpose of the paper.
- Summarize each study, explaining the improvement to outcomes, efficiencies, and lessons learned from the application of the clinical system each peer-reviewed article described. Be specific and provide examples.
- In your conclusion, synthesize the findings from the 4 peer-reviewed research articles.
- Use APA format and include a title page.
- Use the Safe Assign Drafts to check your match percentage before submitting your work.
By Day 7 of Week 8
Submit your completed Assignment.
NURS 6051 Week 9 Discussion: The Inclusion of Nurses in the Systems Development Life Cycle
In the media introduction to this module, it was suggested that you as a nurse have an important role in the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC). With a focus on patient care and outcomes, nurses may not always see themselves as contributors to the development of new systems. However, as you may have observed in your own experience, exclusion of nurse contributions when implementing systems can have dire consequences.
In this Discussion, you will consider the role you might play in systems development and the ramifications of not being an active participant in systems development.
To Prepare:
- Review the steps of the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) as presented in the Resources.
- Reflect on your own healthcare organization and consider any steps your healthcare organization goes through when purchasing and implementing a new health information technology system.
- Consider what a nurse might contribute to decisions made at each stage of the SDLC when planning for new health information technology.
By Day 3 of Week 9
Post a description of what you believe to be the consequences of a healthcare organization not involving nurses in each stage of the SDLC when purchasing and implementing a new health information technology system. Provide specific examples of potential issues at each stage of the SDLC and explain how the inclusion of nurses may help address these issues. Then, explain whether you had any input in the selection and planning of new health information technology systems in your nursing practice or healthcare organization and explain potential impacts of being included or not in the decision-making process. Be specific and provide examples.
By Day 6 of Week 9
Respond to at least two of your colleagues* on two different days, by offering additional thoughts regarding the examples shared, SDLC-related issues, and ideas on how the inclusion of nurses might have impacted the example described by your colleagues.
*Note: Throughout this program, your fellow students are referred to as colleagues.
Example Essay On The Inclusion of Nurses in the Systems Development Life Cycle
The healthcare sector continues to face several unique challenges. There has been an increased demand for enhanced and secure data management methods. There have been many significant advancements in computer technology in the modern world. The use of computers has become ubiquitous across many if not all, sectors. In the healthcare industry, computer technology has revolutionized many practices, increasing efficiency, patient outcomes, communication, and the overall satisfaction levels of healthcare providers and their clients or patients (Mcgonigle & Mastrian, 2022). Nurses form the majority of healthcare providers.
Furthermore, nurses have the most contact and communication with patients. Risling and Risling (2020) assert that nurses play vital roles in decision-making regarding the use of information systems in the healthcare industry and the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC). The SDLC is a cycle involving planning, analyzing, designing, implementing, and maintaining healthcare information systems and nursing informatics (Wang et al., 2019). This paper analyzes the potential repercussions and consequences for organizations that fail to involve nurses in each stage of the SDLC when implementing or purchasing new health information systems.
Planning Phase
The planning phase is an integral part of any project. Effective planning ensures that the subsequent steps run smoothly and ensures the achievement of top-notch results despite the complexity or difficulty of a project. Organizations must conduct a feasibility analysis before implementing or purchasing a new information system. Failing to include nurses in this vital step could lead to developing an ineffective system that does not address all the healthcare organizations. Nurses form most of the healthcare team and spend the most time with patients.
Analysis Phase
The analysis phase entails evaluating a technology to see what works and what does not. In this phase, the project designers examine the requirements and workflows of the new system. Nurses manage patients and also collaborate with other healthcare professionals. Therefore, they understand all healthcare providers’ responsibilities and workflow in patient care. Failing to involve nurses in the analysis phase could lead to developing systems deficient in positive workflows and failing to address all the healthcare needs.
Design Phase
This stage has various processes, including the essentiality of data and program visualization. It also includes how combining different aspects of a system can lead to productive and successful outcomes. Nurses are involved at every point of patient care and know the most essential and non-essential patient data at every interaction phase. Failing to involve nurses in the design phase could lead to a system that is inefficient to use, time-consuming, and fails to collect all essential patient information at different stages.
Implementation and Evaluation Phase
The system developers collaborate with nurses and other healthcare members to bring the new system to life. Failing to involve nurses in this stage can lead to an unhelpful and unfamiliar system that nurses perceive as non-essential to patient care. Hosein et al. (2019) note that nurses dramatically improve healthcare services when they adopt new health information systems. Failing to involve nurses in evaluating the effectiveness of a system can lead to gathering unreliable data that does not identify possible gaps.
The maintenance phase involves continuous user support, which may involve system changes. Failing to involve nurses can lead to long delays in implementing system changes, delaying essential patient care.
I have not yet been involved in developing or selecting a health information technology system. However, there might be some upcoming projects soon. I am positive that I will be involved in the projects. This paper has shed light on the essence of involving nurses in the different phases of the SDLC.
References
Hosein, B., Luo, J., & Karami, M. (2019). Adoption of Hospital Information System Among Nurses: A Technology Acceptance Model Approach. Acta Informatica Medica, 27(5), 305. https://doi.org/10.5455/aim.2019.27.305-310
Mcgonigle, D., & Mastrian, K. G. (2022). Nursing informatics and the foundation of knowledge (5th ed.). Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Risling, T. L., & Risling, D. E. (2020). Advancing nursing participation in user-centered design. Journal of Research in Nursing, 25(3), 226–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744987120913590
Wang, J., Gephart, S. M., Mallow, J., & Bakken, S. (2019). Models of collaboration and dissemination for nursing informatics innovations in the 21st century. Nursing Outlook, 67(4), 419–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.outlook.2019.02.003
NURS 6051 Week 10 Portfolio Assignment: The Role of the Nurse Informaticist in Systems Development and Implementation
Assume you are a nurse manager on a unit where a new nursing documentation system is to be implemented. You want to ensure that the system will be usable and acceptable for the nurses impacted. You realize a nurse leader must be on the implementation team.
To Prepare:
- Review the steps of the Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) and reflect on the scenario presented.
- Consider the benefits and challenges associated with involving a nurse leader on an implementation team for health information technology.
The Assignment: (2-3 pages not including the title and reference page)
In preparation of filling this role, develop a 2- to 3-page role description for a graduate-level nurse to guide his/her participation on the implementation team. The role description should be based on the SDLC stages and tasks and should clearly define how this individual will participate in and impact each of the following steps:
- Planning and requirements definition
- Analysis
- Design of the new system
- Implementation
- Post-implementation support
- Use APA format and include a title page and reference page.
- Use the Safe Assign Drafts to check your match percentage before submitting your work.
By Day 7 of Week 10
Submit your completed Role Description.
NURS 6051 Week 11 Assignment: Policy/Regulation Fact Sheet
As a professional nurse, you are expected to apply your expertise to patient care. On occasion, you will also be expected to share that expertis
READ MORE >>
Assignment: Select a healthcare facility or serviceAssignment: Select a healthca ...
Assignment: Select a healthcare facility or service
Assignment: Select a healthcare facility or service
- Select a healthcare facility or service (e.g., hospital, physician practice, long-term care facility, ambulance service, pharmacy, or skilled nursing facility).
- Identify and read one recently proposed or enacted state or federal legislation that impacts your selected healthcare facility or service.
- Write an 800-word policy brief on the legislation’s effects on your selected facility or service and the state’s population.
Use the following structure when putting together your policy brief:
- Title
- Executive Summary (225 words)
- Recommendations
- Introduction
- State recommendation again
- Body
- Overview of problem
- Review of relevant research
- Application of research results
- Policy Implications
- Conclusion
Cite 3 reputable references to support your assignment (e.g., trade or industry publications, government or agency websites, scholarly works, or other sources of similar quality).
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAY
Assignment: Select a healthcare facility or service Instructions
Read over your paper – in silence and then aloud – before handing it in and make corrections as necessary. Often it is advantageous to have a friend proofread your paper for obvious errors. Handwritten corrections are preferable to uncorrected mistakes.
Use a standard 10 to 12 point (10 to 12 characters per inch) typeface. Smaller or compressed type and papers with small margins or single-spacing are hard to read. It is better to let your essay run over the recommended number of pages than to try to compress it into fewer pages.
Likewise, large type, large margins, large indentations, triple-spacing, increased leading (space between lines), increased kerning (space between letters), and any other such attempts at “padding” to increase the length of a paper are unacceptable, wasteful of trees, and will not fool your professor.
The paper must be neatly formatted, double-spaced with a one-inch margin on the top, bottom, and sides of each page. When submitting hard copy, be sure to use white paper and print out using dark ink. If it is hard to read your essay, it will also be hard to follow your argument.
ADDITIONAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE CLASS
Discussion Questions (DQ)
- Initial responses to the DQ should address all components of the questions asked, include a minimum of one scholarly source, and be at least 250 words.
- Successful responses are substantive (i.e., add something new to the discussion, engage others in the discussion, well-developed idea) and include at least one scholarly source.
- One or two sentence responses, simple statements of agreement or “good post,” and responses that are off-topic will not count as substantive. Substantive responses should be at least 150 words.
- I encourage you to incorporate the readings from the week (as applicable) into your responses.
Weekly Participation
- Your initial responses to the mandatory DQ do not count toward participation and are graded separately.
- In addition to the DQ responses, you must post at least one reply to peers (or me) on three separate days, for a total of three replies.
- Participation posts do not require a scholarly source/citation (unless you cite someone else’s work).
- Part of your weekly participation includes viewing the weekly announcement and attesting to watching it in the comments. These announcements are made to ensure you understand everything that is due during the week.
APA Format and Writing Quality
- Familiarize yourself with APA format and practice using it correctly. It is used for most writing assignments for your degree. Visit the Writing Center in the Student Success Center, under the
- Resources tab in LoudCloud for APA paper templates, citation examples, tips, etc. Points will be deducted for poor use of APA format or absence of APA format (if required).
- Cite all sources of information! When in doubt, cite the source. Paraphrasing also requires a citation.
- I highly recommend using the APA Publication Manual, 6th edition.
Use of Direct Quotes
- I discourage overutilization of direct quotes in DQs and assignments at the Masters’ level and deduct points accordingly.
- As Masters’ level students, it is important that you be able to critically analyze and interpret information from journal articles and other resources. Simply restating someone else’s words does not demonstrate an understanding of the content or critical analysis of the content.
- It is best to paraphrase content and cite your source.
LopesWrite Policy
- For assignments that need to be submitted to LopesWrite, please be sure you have received your report and Similarity Index (SI) percentage BEFORE you do a “final submit” to me.
- Once you have received your report, please review it. This report will show you grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors that can easily be fixed. Take the extra few minutes to review instead of getting counted off for these mistakes.
- Review your similarities. Did you forget to cite something? Did you not paraphrase well enough? Is your paper made up of someone else’s thoughts more than your own?
- Visit the Writing Center in the Student Success Center, under the Resources tab in LoudCloud for tips on improving your paper and SI score.
Late Policy
- The university’s policy on late assignments is 10% penalty PER DAY LATE. This also applies to late DQ replies.
- Please communicate with me if you anticipate having to submit an assignment late. I am happy to be flexible, with advance notice. We may be able to work out an extension based on extenuating circumstances.
- If you do not communicate with me before submitting an assignment late, the GCU late policy will be in effect.
- I do not accept assignments that are two or more weeks late unless we have worked out an extension.
- As per policy, no assignments are accepted after the last day of class. Any assignment submitted after midnight on the last day of class will not be accepted for grading.
Communication
Communication is so very important. There are multiple ways to communicate with me:
- Questions to Instructor Forum: This is a great place to ask course content or assignment questions. If you have a question, there is a good chance one of your peers does as well. This is a public forum for the class.
- Individual Forum: This is a private forum to ask me questions or send me messages. This will be checked at least once every 24 hours.
READ MORE >>
NUR665 Nursing Education Practicum- Week 1 Assignment Nursing Education Practic ...
NUR665 Nursing Education Practicum- Week 1 Assignment Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form
ORDER CUSTOM PAPERS – Assignment: Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form
In your first entry for your Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form you will write the overall goals for your practicum. Only these overall goals are due Week 1 on your NEPD form.
Use the S.M.A.R.T. goal format to write goals you have for your overall practicum experience. What do you want to accomplish during this practicum course? Keep this statement broad enough to cover everything that you would like to do during your practicum course.
You may choose to focus in on a specific aspect of nursing education or may choose to sample a variety of nursing education experiences within your selected practicum experience
APA format is not required, but solid academic writing is expected.

Assignment Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form Directions:
Complete the documentation form. Click on the highlighted text field and type in your response. The form will expand for as long as you type.
Student Name:Semester/Dates of Practicum Course:Overall Practicum Goals: Use the S.M.A.R.T. goal format to write goals you have for your overall practicum experience. Type your five practicum goals in the space below. What do you want to accomplish during this practicum course? Keep this statement broad enough to cover everything that you would like to do during your practicum course. You may choose to focus in on a specific aspect of nursing education or may choose to sample a variety of nursing education experiences within your selected practicum experience.Assignment Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form Learning Goals:What do you want to accomplish during this practicum course? Be sure that your course goals are measurable. Some goals should reflect higher cognitive learning levels in Bloom’s Taxonomy
This column is to be completed before you begin the week’s clinical.
Assignment Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form Resources and Strategies:What type of resources or strategies will you utilize to accomplish your learning goals? Include both human and material resources.This column is to be completed before you begin the week’s clinical.
Assignment Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form Measurement:
How will you know that you have accomplished your learning objective?
What criteria will you use to measure this?
This column is to be completed before you begin the week’s clinical.
Assignment Nursing Education Practicum Documentation (NEPD) Form Evaluation:What did you accomplish that you can use as evidence that you met your learning goals?This column is to be completed after you complete the week’s clinical.
Competency 1 (Week 2) Nurse Educator Competency 1 – Strategies to Facilitate LearningCompetency 1 – Week 2:Date: My objective(s) for this competency is/are to:To meet my weekly goal, I need:I will know I have met my weekly goal when:I know I met/did not meet my weekly goal because:Student weekly reflection analyzing the practicum experience in relation to Competency 1:Clinical Hours completed this Topic:
Total Clinical Hours completed to date:
Date:Faculty Comments:
READ MORE >>
Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative ProposalAssignment – Workplace Safe ...
Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal
Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal
HLT313V Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal
HLT-313v Week 1 Topic 1 Discussion 1
Select and profile (a) a high-level job position you aspire to secure in your chosen allied health field and (b) a same-level position in a different and unrelated allied health care field. What educational and professional qualifications must each individual in this high-level position possess?
What is the typical career path to arrive at each position? Compare and contrast the responsibilities each position entails in regards to workplace safety, risk management, and/or quality of service, and identify one element from each career path that might benefit the other. Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal
HLT-313v Week 1 Topic 1 Discussion 2
Review the biographical sketches of your classmates in this course and select an individual in an allied health career field or position that is different than your own current position or proposed career path. Using your readings, the GCU Library, and Internet association or government websites, identify the safety, risk-management, or quality-based scope of the classmate’s job.
Engage in a dialog with the classmate about whether or not the stated responsibilities are those actually experienced by the individual. How are they the same? How are they different? What “real life” activities in this area does your classmate perform that are not discussed in the official literature? What factors may cause any discrepancies between stated and actual job responsibilities?
CLICK HERE TO ORDER YOUR Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal
HLT-313v Week 1 Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal
Allied health professionals are uniquely qualified in many ways to recommend, implement, and provide valuable feedback regarding safety considerations, risk management, and quality of service across multiple levels within a health care organization.
For this assignment, develop a 1,250-1,500 word proposal inclusive of the following elements:
The proposal identifies and promotes one specific safety, risk management or quality improvement initiative that is recognized or proven to be successful Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal.
The proposed idea would benefit your employer/organization, or if you are not currently employed in this capacity, would benefit an organization in your city/region in your chosen health care field.
The proposal must include and define roles for the organization’s top/corporate management, facility/department management, and the role of the individual allied health professional in implementing the proposed initiative’s activities Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal.
Use the “Topic 1 Assignment Template” for crafting your proposal. Appendices are optional; if needed to support a point or idea in your proposal, please attach tables or graph resources in this section and not in the body of the proposal.
You are required to use and cite a minimum of three qualified resources from the readings or the GCU Library in order to complete this assignment successfully.
Prepare this assignment according to the APA guidelines found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center. An abstract is not required Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to Turnitin. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal.
Also Read:
Discussions Working with Yan Ping Paper
HLT 306V Advanced Patient Care
Assignment Disseminating EBP
Assessment Tool Worksheet Assignment Paper
Assignment Clarifying Research
Policy Patient Safety
In the ever-changing healthcare field, there is a growing emphasis on achieving the Quadruple Aim to facilitate substantial improvements. The Quadruple Aim expands beyond traditional concerns surrounding patient outcomes and encompasses enhancing the patient experience, improving population health, reducing costs, and prioritizing the well-being of healthcare providers (Johnson, 2020). The Quadruple Aim is an augmentation of the Triple Aim (increasing patient experience, improving population health, and lowering costs) to incorporate an extra goal of improving healthcare personnel’s work lives (Arnetz et al., 2020).
Ensuring a positive patient experience involves more than just providing effective treatment; it also entails empathetic communication and strategies that prioritize the needs of patients. At the same time, efforts toward improving population health call for proactive measures like preventive care and community engagement. It is crucial to strike a careful balance by devising cost-effective strategies without compromising the quality of care delivered.
Furthermore, a comprehensive approach is necessary in long-term care settings to fulfill the objectives of the Quadruple Aim. Providing satisfactory experiences for patients becomes crucial as they receive prolonged care. According to Bachynsky (2019), healthcare administrators, especially directors of nursing, are responsible for shaping policies that promote a patient-centered care culture.
At the same time, there is a challenge in maintaining and continuously improving patient safety standards to avoid medical errors among frontline nursing staff members. This article explores practical strategies for implementing the principles of the Quadruple Aim. It examines how healthcare leaders can guide efforts toward cost-effective, high-quality care while prioritizing improved patient satisfaction and enhanced patient safety measures.
Application Of the Principles of The Quadruple Aim Initiative to Improve Quality, Safety, and Satisfaction in The Acute Care or Long-Term Care Setting
The Quadruple Aim is a compass that points the way to comprehensive excellence in the ever-changing healthcare industry. To bring about significant change, exploring how these concepts might be applied in both short-term and long-term care environments is crucial, considering the unique obstacles and possibilities each offers.
Acute Care Setting
In the acute care environment, good communication is critical. Implementing communication training programs for healthcare providers, ensuring empathetic interactions, and actively involving patients in decision-making contribute to a positive patient experience (Ruben et al., 2020). Personalizing treatment regimens according to each patient’s unique requirements, preferences, and cultural norms is important in moving towards a patient-centered approach. As Madden et al. (2021) contend, patients can feel more empowered and actively involved in their care when feedback loops and bedside reporting are integrated.
Proactive healthcare measures can significantly impact population health. Acute care settings can engage in community outreach programs, health education initiatives, and preventive screenings to address health issues before they escalate. By forming alliances with community resources like public health organizations and neighborhood clinics, acute care facilities can expand their impact beyond the confines of the hospital. As Johnson (2020) notes, this collaboration fosters a continuum of care, addressing not only immediate health concerns but also the broader determinants of health.
Efficient resource management is central to cost reduction. Data analytics can be used in acute care settings to determine where resources are wasted, how to improve workflows, and how many staff members are needed (Moreno?Fergusson et al., 2021). The shift to value-based care models encourages healthcare practitioners to focus on cost-effective interventions that meet patient outcomes standards by linking reimbursement to the quality of care rather than the quantity of services (Song et al., 2019).
Acute care facilities should institute policies that put providers’ health first because healthcare is a demanding career. Examples include encouraging a healthy work-life balance, giving resources for mental health, and creating an encouraging environment for employees (Shanafelt et al., 2019). Healthcare practitioners report higher levels of satisfaction and engagement when they have opportunities for continuous professional growth. As Walsh et al. (2019) reiterate, the workforce can benefit from investments in training programs, mentorship activities, and career promotion pathways.
Long-term Care Setting
In settings that provide extended and often chronic care, such as long-term care facilities, the Quadruple Aim specifically focuses on prioritizing patient satisfaction, safety, and the well-being of residents and healthcare providers. To achieve this aim in long-term care settings, it is crucial to prioritize personalized care plans that consider each resident’s specific needs, preferences, and goals (Kwame & Petrucka, 2021). Regularly assessing and adjusting these care plans in collaboration with residents and their families can foster a sense of autonomy and satisfaction.
Loneliness and social isolation are common issues faced by individuals in long-term care—implementing programs that promote social engagement – including group activities and community outings. To enhance patient safety and minimize errors in medication management, healthcare facilities can implement robust systems such as electronic medication administration records barcoding and provide regular staff training. As espoused by Clemson et al. (2019), a comprehensive approach to fall prevention that includes risk assessments, environmental modifications, and staff training can contribute to a safer care environment.
Long-term care settings often face challenges with staffing. Organizations can positively impact staff satisfaction and retention by implementing supportive staffing models considering workload, adequate staffing ratios, and professional development opportunities (Demiris et al., 2020). Fostering a collaborative team environment where different healthcare professionals work together seamlessly promotes shared responsibility and support. Regular interdisciplinary team meetings and open communication channels contribute to cultivating a positive work culture within the organization. By incorporating these principles into their daily operations, healthcare leaders can create environments prioritizing patient experience, safety, and satisfaction while considering the healthcare workforce’s well-being.
The Role of a Healthcare Administrator
Beyond administrative duties, a potential director of nursing or healthcare administrator must be dedicated to promoting excellence in healthcare delivery. This includes taking a proactive and strategic approach to improving patient safety, cost-effective quality care, and patient satisfaction. According to Johnson (2020), optimizing resource utilization would be paramount to a healthcare leader. This entails putting data-driven ideas into practice to find inefficiencies, optimize operations, and raise the standard of care given.
Working with interdisciplinary teams, I would promote evidence-based procedures and technology that enhance patient outcomes while lowering costs over the long run. Maintaining sustained quality in patient care while optimizing resource efficiency would require implementing continual quality improvement activities and routinely evaluating the effectiveness of treatment regimens.
Patient satisfaction is deeply intertwined with the overall healthcare experience. I would support improving patient engagement, communication, and transparency to raise satisfaction levels. By using patient feedback tools like focus groups and questionnaires, healthcare providers can gain important insights that can be used to customize patient treatment (Ruben et al., 2020). Furthermore, promoting a patient-centered culture among medical personnel via continual education and acknowledgment initiatives will help create a setting where patients’ needs and preferences are prioritized.
As far as healthcare administration is concerned, patient safety cannot be compromised. I would advocate for implementing robust patient safety protocols, leveraging technology for error reduction, and fostering a culture of accountability. A thorough patient safety policy would include ongoing training for frontline staff, event reporting systems, and regular safety audits (Johnson, 2020). Engaging in proactive risk management and ensuring safe and effective healthcare by collaborating with quality improvement teams and remaining up to date on the newest developments in healthcare safety practices is imperative.
As a director of nursing or healthcare administrator, my job would entail strategic decision-making and active participation in creating a healthcare environment that places a premium on high patient satisfaction, cost-effective quality care, and a steadfast dedication to patient safety. I want to help achieve the Quadruple Aim by bringing together leadership, teamwork, and a commitment to ongoing development. This will help create a healthcare environment that is effective but also patient-centered and compassionate.
Minimizing Medical Errors Among Frontline Nursing Staff
A comprehensive and proactive approach is necessary to reduce medical errors among frontline nursing staff. This includes implementing extensive training programs, integrating technology effectively, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement. As a healthcare leader, it is essential to implement specific strategies prioritizing patient safety within the organization.
Implementing comprehensive and continuous training programs for frontline nursing staff is essential. These programs should focus on technical skills and emphasize critical thinking, situational awareness, and effective communication (Clemson et al., 2019). Integration of simulation exercises, reflective learning sessions, and case reviews will be crucial components as they allow nurses to learn from real-life scenarios in a controlled setting. Ongoing education ensures that staff members stay updated on best practices and promotes a culture of learning and adaptability.
Medication mistakes essentially cause adverse events. Error risk can be significantly decreased by putting technology solutions like barcoding systems, computerized physician order entry (CPOE), and electronic medication administration records (eMAR) into practice. By offering dose checks, real-time verification, and alarms for possible drug interactions, these systems improve the precision and security of medication administration (Moreno?Fergusson et al., 2021).
Creating effective channels of communication is essential in preventing and addressing medical errors. Encouraging an atmosphere that allows frontline nursing staff to report mistakes openly, without fear of negative consequences, promotes transparency within healthcare organizations (Fencl et al., 2021). Regular team huddles, debriefings, and fostering an environment where questions are welcomed help proactively identify and address potential issues.
Healthcare organizations must adopt a systematic approach to root cause analysis following any identified medical error. According to Singh et al. (2021), this includes conducting comprehensive investigations to determine the underlying causes and implementing corrective measures to prevent future occurrences. Furthermore, fostering a culture of continuous improvement encourages staff members to contribute to identifying potential risks and proposing innovative solutions actively. Regular review meetings and feedback loops significantly create an environment prioritizing learning from mistakes.
Effective interdisciplinary collaboration is crucial in preventing medical errors. This can be achieved through regular team meetings, joint training sessions, and fostering a culture of mutual respect and shared responsibility. By promoting open communication and coordination among healthcare professionals from different departments, the likelihood of errors due to miscommunication or lack of coordination can be reduced (Ruben et al., 2020). Investing in continuous training, embracing technology solutions, conducting thorough error analyses, and promoting interdisciplinary collaboration are key strategies that healthcare leaders can implement to prioritize patient safety and mitigate the risk of medical errors at the front lines of care.
Conclusion
As a paradigm, the Quadruple Aim goes beyond typical measurements, including patient experience, population health, cost savings, and provider well-being. A holistic approach to acute treatment is required, emphasizing compassionate communication and preventive community health interventions. Long-term care necessitates personalized plans, social involvement, and stringent safety precautions. As healthcare administrators, particularly as directors of nursing, it is critical to optimize resources, develop patient-centered cultures, and prioritize safety. This investigation demonstrates the commitment to holistic healthcare, adding to ongoing discussions about efficient, compassionate, and patient-centered healthcare delivery.
Assignment – Workplace Safety Initiative Proposal References
Arnetz, B. B., Goetz, C. M., Arnetz, J. E., Sudan, S., vanSchagen, J., Piersma, K., & Reyelts, F. (2020). Enhancing healthcare efficiency to achieve the quadruple aim: An exploratory study. BMC Research Notes, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-020-05199-8
Bachynsky, N. (2019). Implications for policy: The triple aim, quadruple aim, and interprofessional collaboration. Nursing Forum, 55(1), 54–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/nuf.12382
Clemson, L., Stark, S., Pighills, A. C., Torgerson, D. J., Sherrington, C., & Lamb, S. E. (2019). Environmental interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2023(2). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd013258
Demiris, G., Hodgson, N. A., Sefcik, J. S., Travers, J. L., McPhillips, M. V., & Naylor, M. D. (2020). High-value care for older adults with complex care needs: Leveraging nurses as innovators. Nursing Outlook, 68(1), 26–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.outlook.2019.06.019
Fencl, J. L., Willoughby, C., & Jackson, K. (2021). Just culture: The foundation of staff safety in the perioperative environment. AORN Journal, 113(4), 329–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/aorn.13352
Johnson, S. (2020). The Quadruple Aim in Nursing and Healthcare: Improving Care, Lowering Costs, Serving Populations, Elevating Work Life. In Google Books. McFarland. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=xDnlDwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=The+Quadruple+Aim+expands+beyond+traditional+concerns+surrounding+patient+outcomes+and+encompasses+enhancing+the+patient+experience
Kwame, A., & Petrucka, P. M. (2021). A literature-based study of patient-centered care and communication in nurse-patient interactions: Barriers, facilitators, and the way forward. BMC Nursing, 20(158), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-021-00684-2
Madden, C., Lydon, S., Murphy, A. W., & O’Connor, P. (2021). Patients’ perception of safety climate in Irish general practice: A cross-sectional study. BMC Family Practice, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12875-021-01603-9
Moreno?Fergusson, M. E., Guerrero Rueda, W. J., Ortiz Basto, G. A., Arevalo Sandoval, I. A. L., & Sanchez–Herrera, B. (2021). Analytics and lean health care to address nurse care management challenges for inpatients in emerging economies. Journal of Nursing Scholarship, 53(6), 803–814. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnu.12711
Ruben, M. A., Blanch?Hartigan, D., & Hall, J. A. (2020). Communication skills to engage patients in treatment. The Wiley Handbook of Healthcare Treatment Engagement, 274–296. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119129530.ch15
Shanafelt, T. D., West, C. P., Sinsky, C., Trockel, M., Tutty, M., Satele, D. V., Carlasare, L. E., & Dyrbye, L. N. (2019). Changes in burnout and satisfaction with work-life integration in physicians and the general US working population between 2011 and 2017. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 94(9). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.10.023
Singh, G., Patel, R. H., & Boster, J. (2021). Root cause analysis and medical error prevention. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570638/
Song, Z., Ji, Y., Safran, D. G., & Chernew, M. E. (2019). Health care spending, utilization, and quality 8 years into global payment. New England Journal of Medicine, 381(3), 252–263. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmsa1813621
Walsh, A. L., Lehmann, S., Zabinski, J., Truskey, M., Purvis, T., Gould, N. F., Stagno, S., & Chisolm, M. S. (2019). Interventions to prevent and reduce burnout among undergraduate and graduate medical education trainees: A systematic review. Academic Psychiatry, 43(4), 386–395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40596-019-01023-z
READ MORE >>
Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313VBenchmark Assi ...
Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal, HLT313V
Benchmark Assignment – Performance Management Plan ProposalPerformance management is, ideally, an ongoing quality-assurance-based process to provide an organization, its employees, regulatory agencies, accreditors, and other stakeholders with a structured means to support and accomplish mutually identified strategic goals and objectives.
Assume the role of a newly-hired risk management officer for a hypothetical new allied health organization in your chosen career field. You and your team will need to develop the organization’s policies.
The first item you will create will be a performance management plan. Using the resources in HIM Briefings or other qualified framework, craft a proposal (1,250-1,500 words) for a performance management plan for the new organization that includes the following: Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
- Organizational Goals: Provide a statement of the organization’s goals in terms of workplace safety, risk management, or quality improvement. Select one area, and develop five goals for that one area.
- Outline of Organizational Objectives: Outline and provide a brief evaluation of specific objectives that support the organizational goals you previously identified to include the use of a interdisciplinary approach to patient care.
- Rationale: Evaluate the use of the interdisciplinary approach to patient care in the performance management plan. When provisions were planned in order to include this approach effectively.
- Quality and Process Outcomes: Describe the importance of quality and process outcomes within one’s scope of practice.
- Summary of Relevant Performance Measures: Summarize the steps and measures the new organization will adopt to measure performance. Consider (a) how well measures will align with the stated goals, (b) how these measures demonstrate the importance of quality, and the relationship to positive health outcomes, (c) how the measures are able to be controlled by the organization (i.e., how the organization can effect change in this area), and (d) how the measures meet criteria related to reliability and validity, and which are standardized.
- Performance Baseline: Determine a performance baseline for the measures selected. This will enable the organization to conduct comparisons of desired goals versus actual results over time.
- Performance Evaluation: Select one of three commonly accepted methods to measure provider quality and summarize the features and why it applies best to the organization. Refer to the assigned reading, “The Measurement of Health Care Performance: A Primer from the Council of Medical Specialty Societies.”
- Definition of Success: Define what success means to the organization. Now that you have chosen measures to assess organizational performance, identify what success means to the organization; otherwise, you are chasing a moving target. Be explicit in the level of performance you see as acceptable. This will change as an organization grows, but you need to start somewhere in order to get anywhere.
Provide a minimum of three qualified resources from the readings, qualified websites, or the GCU Library in order to complete this assignment successfully.
Prepare this assignment according to the guidelines found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center. An abstract is not required.
This assignment uses a rubric. Review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Refer to the LopesWrite Technical Support articles for assistance.
Benchmark Information:
This benchmark assignment assesses the following programmatic competencies:
BS – Homeland Security and Emergency Management
1.4: Evaluate the use of an interdisciplinary approach to patient care.
5.3: Describe the importance of quality and process outcomes within one’s scope of practice.
Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V RUBRIC
Course CodeClass CodeAssignment TitleTotal PointsHLT-313VHLT-313V-O500Benchmark Assignment – Performance Management Plan Proposal200.0CriteriaPercentageUnsatisfactory (0.00%)Less Than Satisfactory (65.00%)Satisfactory (75.00%)Good (85.00%)Excellent (100.00%)CommentsPoints EarnedContent70.0%Organizational Goals10.0%Proposal does not include a discussion of organizational goals.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313VProposal includes a discussion with specific organizational goals, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes a basic discussion with specific organizational goals. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal includes a complete discussion with specific organizational goals. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes a clear and thorough discussion with specific organizational goals. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Outline of Organizational Objectives10.0%Proposal does not include an outline of organizational objectives.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Proposal includes an outline of organizational objectives, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes an outline and brief evaluation of organizational objectives. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Proposal includes an outline and brief evaluation of organizational objectives. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes an outline and brief evaluation of organizational objectives. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Rationale (C1.4)10.0%Proposal does not include an evaluation of the use of the interdisciplinary approach.Proposal includes an evaluation of the use of the interdisciplinary approach, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes an evaluation of the use of the interdisciplinary approach. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal includes an evaluation of the use of the interdisciplinary approach. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes an evaluation of the use of the interdisciplinary approach. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Quality and Process Outcomes (C5.3)10.0%Proposal does not include a description of the importance of quality and process outcomes within the scope of practice.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Proposal includes a description of the importance of quality and process outcomes within the scope of practice, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes a description of the importance of quality and process outcomes within the scope of practice. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal includes a description of the importance of quality and process outcomes within the scope of practice. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes a description of the importance of quality and process outcomes within the scope of practice. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Summary of Relevant Performance Measures8.0%Proposal does not include a summary of relevant performance measures.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Proposal includes a summary of relevant performance measures, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes a summary of relevant performance measures. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal includes a complete summary of relevant performance measures. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes a clear and thorough summary of relevant performance measures. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Performance Baseline7.0%Proposal does not identify or include a performance baseline.Proposal identifies a performance baseline, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal identifies and includes a performance baseline. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal identifies and includes a performance baseline. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal identifies and includes a performance baseline. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Performance Evaluation8.0%Proposal does not include a discussion of a method of performance evaluation.Proposal includes a discussion of a method of performance evaluation, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes a basic discussion of a method of performance evaluation. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal includes a complete discussion of a method of performance evaluation. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes a clear and thorough discussion of a method of performance evaluation. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Definition and Discussion of Success7.0%Proposal does not include define or include a discussion of success for the organization.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Proposal includes a definition and/or a discussion of success for the organization, but elements are missing or the submission is otherwise incomplete.Proposal includes a basic definition and discussion of success for the organization. Minimal detail and/or support are provided.Proposal includes a complete definition and discussion of success for the organization. Proposal incorporates most essential details and provides appropriate support.Proposal includes a clear and thorough definition and discussion of success for the organization. Proposal analyzes supporting evidence insightfully and provides specific examples with relevance. Level of detail is appropriate.Organization and Effectiveness20.0%Thesis Development and Purpose7.0%Paper lacks any discernible overall purpose or organizing claim.Thesis is insufficiently developed or vague. Purpose is not clear.Thesis is apparent and appropriate to purpose.Thesis is clear and forecasts the development of the paper. Thesis is descriptive and reflective of the arguments and appropriate to the purpose.Thesis is comprehensive and contains the essence of the paper. Thesis statement makes the purpose of the paper clear.Argument Logic and Construction8.0%Statement of purpose is not justified by the conclusion. The conclusion does not support the claim made. Argument is incoherent and uses noncredible sources.Sufficient justification of claims is lacking. Argument lacks consistent unity. There are obvious flaws in the logic. Some sources have questionable credibility.Argument is orderly, but may have a few inconsistencies. The argument presents minimal justification of claims. Argument logically, but not thoroughly, supports the purpose. Sources used are credible. Introduction and conclusion bracket the thesis.Argument shows logical progression. Techniques of argumentation are evident. There is a smooth progression of claims from introduction to conclusion. Most sources are authoritative.Clear and convincing argument presents a persuasive claim in a distinctive and compelling manner. All sources are authoritative.Mechanics of Writing (includes spelling, punctuation, grammar, language use)5.0%Surface errors are pervasive enough that they impede communication of meaning. Inappropriate word choice and/or sentence construction are used.Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
Frequent and repetitive mechanical errors distract the reader. Inconsistencies in language choice (register) and/or word choice are present. Sentence structure is correct but not varied.Some mechanical errors or typos are present, but are not overly distracting to the reader. Correct and varied sentence structure and audience-appropriate language are employed.Prose is largely free of mechanical errors, although a few may be present. The writer uses a variety of effective sentence structures and figures of speech.Writer is clearly in command of standard, written, academic English.Format10.0%Paper Format (Use of appropriate style for the major and assignment)5.0%Appropriate template is not used appropriately or documentation format is rarely followed correctly.Appropriate template is used, but some elements are missing or mistaken; lack of control with formatting is apparent.Appropriate template is used, and formatting is correct, although some minor errors may be present.Appropriate template is fully used; There are virtually no errors in formatting style.All format elements are correct.Documentation of Sources (citations, footnotes, references, bibliography, etc., as appropriate to assignment and style)5.0%Sources are not documented.Documentation of sources is inconsistent or incorrect, as appropriate to assignment and style, with numerous formatting errors.Sources are documented, as appropriate to assignment and style, although some formatting errors may be present.Sources are documented, as appropriate to assignment and style, and format is mostly correct.Sources are completely and correctly documented, as appropriate to assignment and style, and format is free of error.Total Weightage100%
Week 5 Required Resources – Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
McLaughlin and Kaluzny’s Continuous Quality Improvement in Health CareRead Chapters 12 and 14 from McLaughlin and Kaluzny’s Continuous Quality Improvement in Health Care.
URL:
https://www.gcumedia.com/digital-resources/jones-and-bartlett/2018/mclaughlin-and-kaluznys-continuous-quality-improvement-in-health-care-custom_5e.php
Performance Management and MeasurementRead “Performance Management and Measurement,” located on the Health Resources and Services Administration website.
URL:
https://www.hrsa.gov/sites/default/files/quality/toolbox/508pdfs/performancemanagementandmeasurement.pdf
Meet HIM Department Goals with a Performance Management ProgramUse “Meet HIM Department Goals with a Performance Management Program,” from HIM Briefings (2019) to complete your assignment.
URL:
https://lopes.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=136952250&site=ehost-live&scope=site
PCMH Accreditation Becomes More FlexibleRead “PCMH Accreditation Becomes More Flexible,” by Terry, from Medical Economics (2017).
URL:
https://lopes.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ofs&AN=122635935&site=ehost-live&scope=site
The JRCERT Accreditation Process: A Site Visitor’s PerspectiveRead “The JRCERT Accreditation Process: A Site Visitor’s Perspective,” by Zelna and Schans, from Radiologic Technology (2017).
URL:
https://lopes.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=120516430&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Integrating Purpose with a Mission Statement: When Structured and Applied, Quality and Performance Improvement Value Are CreatedRead “Integrating Purpose with a Mission Statement: When Structured and Applied, Quality and Performance Improvement Value are Created,” by Kern, from Healthcare Executive (2018).
URL:
https://lopes.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ccm&AN=132751339&site=ehost-live&scope=site
The Measurement of Health Care Performance: A Primer From the Council of Medical Specialty SocietiesRead “The Measurement of Health Care Performance: A Primer From the Council of Medical Specialty Societies,” from Council of Medical Specialty Societies (2015).
URL:
https://cmss.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/CMSS-Quality-Primer-layout.final_-1.pdf
Optional – Key Performance IndicatorsFor additional information, the following is recommended: “Key Performance Indicators,” by Walston, from Organizational Behavior and Theory in Healthcare: Leadership Perspectives and Management Applications (2017)
URL:
https://lopes.idm.oclc.org/login?url=http://library.books24x7.com.lopes.idm.oclc.org/library.asp?^B&bookid=142877&chunkid=542537354&rowid=445
Benchmark Assignment Performance Management Plan Proposal HLT 313V
READ MORE >>
Becoming a licensed surgical nurse takes at least four years if you are not alre ...
Becoming a licensed surgical nurse takes at least four years if you are not already a registered nurse. The first step is to earn an associate’s degree, which qualifies you to take the NCLEX-RN exam. After passing the exam, you’ll need to gain two years of hands-on experience working as a registered nurse before you can apply for surgical nurse certification.
If you opt to pursue a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) instead of an associate’s degree, the entire process will take around six years to become a certified perioperative nurse.
The certification path for registered nurses who want to specialize in surgical nursing involves acquiring the necessary perioperative experience, which can vary depending on the certification. Those who wish to become a Certified Registered Nurse First Assistant (CRNFA) must hold a bachelor’s degree and meet the experience requirements.
Who is a Surgical Nurse?
A surgical nurse, also known as a perioperative nurse, is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care to patients undergoing surgical procedures. They play a vital role in ensuring the safety and well-being of patients before, during, and after surgery.
What Do Surgical Nurses Do?
Here are some of the key responsibilities of a surgical nurse:
Pre-operative care
- Educating, counseling, and reassuring patients before their surgeries
- Assessing and recording patients’ vital signs and medical histories
- Preparing the operating room by setting up instruments and equipment
- Sterilizing and marking incision sites
- Assisting in setting up intravenous lines and other necessary equipment
Intra-operative care:
- Monitoring patients’ vital signs during surgery
- Assisting the surgical team by passing instruments and supplies
- Maintaining a sterile environment to prevent infections
- Assisting anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists in monitoring the patient’s anesthesia
- Helping to position the patient according to the surgical procedure
- Resuscitating patients if necessary
Post-operative care
- Transporting patients to recovery rooms or intensive care units
- Monitoring patients’ vital signs and overall condition after surgery
- Administering medications and fluids as prescribed
- Changing dressings and monitoring surgical sites for signs of infection
- Educating patients and their families about post-operative care and recovery
Surgical nurses work closely with surgeons, anesthetists, and other healthcare professionals to ensure that patients receive the highest quality care throughout their surgical journey. Their expertise and attention to detail prevent complications and promote optimal patient outcomes.
Steps to Becoming a Surgical Nurse
Becoming a surgical nurse involves a combination of education, experience, and specialized training. Here’s a detailed guide on how to pursue a career in surgical nursing:
Earn a Nursing Degree
The first step to becoming a surgical nurse is to obtain a nursing degree from an accredited college or university. You can choose an Associate’s Degree in Nursing (ADN) or a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN). While some hospitals hire ADN nurses, most prefer candidates with a BSN, as it better prepares you for the complexities of surgical nursing.
Obtain RN Licensure
After completing your nursing degree, you must pass the National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN). This nationwide exam is a requirement for practicing as a registered nurse in the United States.
Gain Relevant Experience
Most hospitals and surgical centers require nurses to have at least one year of relevant experience before transitioning into a perioperative role. Gain experience in medical-surgical nursing, critical care, or emergency nursing to build a strong foundation for your surgical nursing career.
Pursue Specialized Training
To prepare for a surgical nursing role, consider attending a specialized training program like the “Periop101: A Core Curriculum” offered by the Association of Perioperative Registered Nurses (AORN). This program covers essential topics like anesthesia, surgical draping, and patient and equipment safety.
Obtain Certification
After gaining experience in perioperative nursing, you can demonstrate your expertise and enhance your career prospects by obtaining certification. The Competency and Credentialing Institute (CCI) offers three perioperative nursing certifications:
CNOR (Certified Perioperative Nurse): This certification is designed for surgical nurses with at least two years of perioperative experience and validates their skills and knowledge.
CFPN (Certified Foundational Perioperative Nurse): This credential is intended for surgical nurses with less than two years of experience and provides a foundation for ongoing professional development.
CNAMB (Certified Ambulatory Surgery Nurse): This certification recognizes perioperative nurses’ specialized knowledge and competencies working in ambulatory surgery settings.
Additionally, nurses interested in post-operative care and patient education may pursue the Certified Medical-Surgical Registered Nurse (CMSRN) certification offered by the Academy of Medical-Surgical Nurses. To be eligible, candidates must have an active RN license, two years of med-surg experience, and at least 2,000 hours of practice in the past three years.
By following these steps and continuously seeking opportunities for growth and learning, you can build a rewarding career as a skilled and knowledgeable surgical nurse.
How Much do Surgical Nurses Make?
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for registered nurses, including surgical nurses, was $77,600 in May 2021. However, surgical nurses with advanced certifications and experience can earn higher salaries, ranging from $80,000 to over $100,000 annually, depending on location, employer, and specialization.
Can you become a Surgical Nurse online?
While you can complete some nursing degree programs online, becoming a surgical nurse requires hands-on clinical experience that cannot be fully replicated online. However, some universities offer hybrid programs that combine online coursework with in-person clinical rotations. After becoming a registered nurse, you can pursue additional online courses or certifications to specialize in surgical nursing.
What is the difference between a Surgical Nurse and a Scrub Nurse?
A surgical nurse is a broad term that encompasses all nurses who work in the perioperative setting, including pre-operative, intra-operative, and post-operative care. A scrub nurse, also known as an operating room nurse or perioperative nurse, is a specific type of surgical nurse who works directly with the surgical team during an operation. Scrub nurses are responsible for maintaining a sterile environment, preparing and handling surgical instruments, and assisting the surgeon during the procedure.
Do your Surgical Nurse exam qualifications expire?
Most surgical nurse certifications, such as the CNOR (Certified Perioperative Nurse) or CRNFA (Certified Registered Nurse First Assistant), require periodic renewal to ensure that nurses maintain their knowledge and skills. Renewal requirements often involve completing a certain number of continuing education hours and/or retaking the certification exam. The specific renewal period and requirements vary depending on the certifying organization.
Is Surgical Nursing Difficult?
Surgical nursing can be challenging, as it requires a high level of technical skill, attention to detail, and the ability to work well under pressure. Surgical nurses must have a strong understanding of anatomy, physiology, and surgical procedures, as well as the ability to anticipate the needs of the surgical team and respond quickly to emergencies. They also need excellent communication and interpersonal skills to effectively collaborate with other healthcare professionals and provide compassionate patient care. While the demands of surgical nursing can be significant, many nurses find the work highly rewarding and fulfilling.
How many years does it take to become a surgical nurse?
It takes 4-6 years to become a surgical nurse. This includes:
- 2-4 years to earn a nursing degree (ADN or BSN)
- Passing the NCLEX-RN exam
- 1-2 years of experience in general nursing
- Additional specialized training in perioperative nursing, often through a 6-12 month program
Some nurses may take longer if they pursue advanced certifications or a master’s degree. The exact timeline can vary based on individual circumstances, the educational path chosen, and specific employer requirements.
READ MORE >>
Assignment 6: Perceiving and BelievingAssignment 6: Perceiving and BelievingTo r ...
Assignment 6: Perceiving and Believing
Assignment 6: Perceiving and Believing
To relate the material in Chapter Four, “Perceiving and Believing,” to the assigned film. Your paper (3-4 pages) will consist of three sections as follows.
- Introduction Paragraph (2 pts.)
- Briefly summarize the film in five sentences or less.
- Thinking (6 pts.)
- What was the event that inspired the film
- What caused the event
- What was the response
- How did different points of view include factual reports, inductive inferences, evaluative judgments
- How do perceptions and beliefs of others influence awareness of our “lenses?”
- Conclusion Paragraph (2 pts.)
- Briefly explain how the text relates to the reader in Chapter Four, “Perceiving and Believing.”
ORDER THROUGH BOUTESSAY
- What was the event that inspired the film
- What caused the event
- What was the response
- How did different points of view include factual reports, inductive inferences, evaluative judgments
- How do perceptions and beliefs of others influence awareness of our “lenses?”
- Conclusion Paragraph (2 pts.)
- Briefly explain how the text relates to the text in Chapter Four, “Perceiving and Believing.”
Chapter 4
Things aren’t always what they seem! This “Mae West Room” in the Salvador Dali Museum illustrates the complex and surprising nature of perceiving and making sense of our world. How do we develop clear and accurate perceptions of the world that are not biased or slanted toward one perspective?
Perceiving is actively selecting, organizing, and interpreting sensations: selecting to pay attention to, collecting sensations into a design or pattern, and interpreting what this pattern or event means.
Experiences shape our perceptions. We view the world through our unique lenses, which shape and influence our perceptions. We construct beliefs based on our perceptions. We construct knowledge based on our beliefs. Thinking critically involves understanding how lenses influence perceptions, beliefs, and learning.
Thinking is how you make sense of the world. By believing in an active, purposeful, and organized way, you can solve problems, work toward your goals, analyze issues, and make decisions.
Your experience of the world comes to you by means of your senses: sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. These senses are your bridges to the world, making you aware of what occurs outside you; the process of becoming aware of your world through your senses is known as perceiving.
In this chapter, you will explore how your perceiving process operates, how your perceptions lead to the construction of your beliefs about the world, and how your perceptions and your beliefs relate to your ability to think effectively.
In particular, you will discover how you shape your personal experience by actively selecting, organizing, and interpreting the sensations the senses provide. We each view the world through a pair of individual “eyeglasses” or “lenses” that reflect our past experiences and unique personalities.
As a critical thinker, you want to become aware of the nature of your lenses to help eliminate any bias or distortion they may be causing. You also want to become aware of the lenses of others so that you can better understand why they view things the way they do.
At almost every waking moment of your life, your senses are bombarded by many stimuli: images to see, noises to hear, odors to smell, textures to feel, and flavors to taste. The experience of all these sensations at once creates what the nineteenth-century American philosopher William James called “a bloomin’ buzzin’ confusion.” Yet to us, the world usually seems much more orderly and understandable. Why is this so?
First, your sense equipment can receive sensations only within certain limited ranges. For example, animals can detect many sounds and smell that you cannot because their sense organs have broader ranges than yours.
A second reason you can handle this sensory bombardment is that from the stimulation available, you select only a small amount on which to focus your attention. To demonstrate this, try the following exercise.
Concentrate on what you can see, ignoring your other senses. Focus on sensations you were unaware of and then answer the first question. Concentrate on each of your other senses in turn, following the same procedure.
1. What can you see? (e.g., the shape of the letters on the page, the design of the clothing on your arm)
2. What can you hear? (e.g., the hum of the air conditioner, the rustling of a page)
3. What can you feel? (e.g., the pressure of the clothes against your skin, the texture of the page, the keyboard against your fingers)
4. What can you smell? (e.g., the perfume or cologne someone is wearing, the odor of stale cigarette smoke)
5. What can you taste? (e.g., the aftereffects of your last meal)
Compare your responses with those of the other students in the class. Do your classmates perceive sensations that differ from the ones you perceived? If so, how do you explain these differences?
As you perform this simple exercise, it should become clear that for every sensation you focus your attention on, countless other sensations are ignored.
You would be completely overwhelmed if you knew everything is happening at every moment. By selecting certain sensations, you can make sense of your world in a relatively orderly way. The activity of using your senses to experience and make sense of your world is known as perceiving.
READ MORE >>
Benchmark – Population Health Policy Analysis Essay NUR 550 ExampleDiabetes af ...
Benchmark – Population Health Policy Analysis Essay NUR 550 Example
Diabetes affects more than 30 million Americans and costs the country more than “$327 billion per year” (Cefalu, 2018). Diabetes has a significant impact on people’s lives, resulting in increased medical costs, lost productivity, premature deaths, and decreased quality of life. Diabetes is not going away, and the patient population has grown. Unfortunately, so has the cost of the life-saving drug insulin.
Rising insulin costs, an essential medication that has more than tripled in price, are making life difficult for diabetics. Some are even forced to choose between buying their medications and paying for other necessities, putting their health at risk in the short and long term. The question is, why has a medication that was invented in the 1920s and has seen few changes become increasingly expensive, and what can we do to help offset those costs?
History of Insulin
The discovery of insulin in 1922 marked a major breakthrough in medicine and therapy in patients with diabetes. Long before the discovery of insulin, it was hypothesized that the pancreas secreted a substance that controlled carbohydrate metabolism. For years, attempts at preparing pancreatic extracts to lower blood glucose were unsuccessful due to impurities and toxicities.
It was Frederick Banting, an orthopedic surgeon, who first isolated the pancreatic islet extracts from the pancreatic duct of dogs (Quianzon, n.d.). Relatively few changes have happened to insulin since its invention, save for the introduction of some preservatives that enabled it to act longer. Finally, in 1982 we were able to ‘create’ a human analogue of the insulin, and there have been no real changes since (Quianzon, n.d.).

Improving Access
In the spring of 2017, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Board of Directors convened an ‘Insulin Access and Affordability Working Group’ (Working Group) to determine the full scope of the insulin affordability problem. Their main goal was to recommend “strategies, and to provide high-level direction to the ADA related to this issue” (Cefalu, 2018). One major finding of the Working Group was that the average price of insulin nearly tripled between 2002 and 2013 in the United States, yet other countries pay significantly less.
In fact, “Americans pay more than 10 times as much for insulin as Canadians do, according to a commentary published in the Nov. 7 issue of the New England Journal of Medicine, despite a single vial of current analog insulin only costing around $3 to $6 to make” (Healthday, 2019). Because of this, lawmakers in the US are trying to stop ‘price-gouging’ and regulate the costs of insulin.
Addressing the Issue
In an era when healthcare is extremely expensive, there are many opinions on how involved our federal government should be in bringing drug prices down. However, there is one particular drug-pricing crisis that many can agree needs to be addressed sooner rather than later: the insulin crisis. New legislation in Washington and Colorado cap the price of insulin at $100 per 30-day supply, and several federal bills have also been introduced.
While none of the bills specify how they make this work, they have created a law “cap[ping] the total amount that a covered person is required to pay for a covered prescription insulin drug at an amount not to exceed one hundred dollars per thirty-day supply of insulin, regardless of the amount or type of insulin needed to fill the covered person’s prescription” (Roberts et al, 2019).
Implications
If we don’t put an end to unnecessarily high insulin costs, many more people will lose the fight against diabetes, succumbing to problems associated with a lack of insulin. While these measures suggest there’s finally some attention and progress on the issue of insulin price gouging, there are several significant things to consider: Colorado and Washington are just two states, and people with diabetes live in all over the US, and these caps only apply to people who have health insurance coverage. For people without insurance, or those living outside of the states, mentioned, they continue to face high costs with no clear end in sight.
While much of the cost of diabetes appears to fall on insurers (especially Medicare) and employers (in the form of reduced productivity at work, missed work days, and higher employer costs for health care), in reality such costs are passed along to all of society in the form of higher insurance premiums and taxes, reduced earnings, and reduced standard of living.
Patient Advocacy
As an APRN we are responsible for ensuring that our patients receive the best care possible. This includes providing them with the different ways they can get access to their medications. Until there is a ‘universal’ health care and coverage program, then we have to be ready to help patients find things like rebates, coupons, sponsorships, etc for their more expensive medications – medications like insulin. Directing patients to the these programs can help them mitigate the costs of their disease and improve quality of life.
Conclusion
“Insulin is a flashpoint in the drug-pricing debate, and it’s still an ongoing issue. It’s a relatively unique product that will require special solutions because so many people rely on it to ensure they can live day to day,” said commentary co-author Dr. Aaron Kesselheim, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School (HealthDay, 2019).
Dramatic improvements in how we treat diabetes have transformed the lives of patients, but this innovation isn’t enough if patients can’t afford their insulin and other medicines at the pharmacy. While the bills introduced are a start, we still have a long way to go.
Benchmark – Population Health Policy Analysis Essay NUR 550 References
- American Diabetes Association. (1 Jun. 2018.) “Economic Costs of Diabetes in the U.S. in 2017.” Diabetes Care. American Diabetes Association. Web. 30 Jan. 2020. Https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/5/917
- Beran, David. (1 Jun. 2018.) “Why Are We Failing to Address the Issue of Access to Insulin? A National and Global Perspective.” Diabetes Care. American Diabetes Association. Web. 30 Jan. 2020. <https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/6/1125>
- Cefalu, Wiliam.( 1 Jun. 2018.) “Insulin Access and Affordability Working Group: Conclusions and Recommendations.” Diabetes Care. American Diabetes Association, Web. 30 Jan. 2020. Https://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/41/6/1299
- Healthday. (2019). Why Are Insulin Prices Still So High for U.S. Patients? Retrieved January 30, 2020, from US News & World Report website: https://www.usnews.com/news/health-news/articles/2019-11-07/why-are-insulin-prices-still-so-high-for-us-patients
- Quianzon, Celeste C. (n.d.) “History of insulin.” pubmed Central (PMC). Taylor & Francis, Web. 30 Jan. 2020. Https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3714061/
- Roberts, Arndt, Caraveo, Coleman, Galindo, G., Gonzales-Gutierrez, … Bridges, P. (2019.). House Bill 19-1216. Retrieved from https://leg.colorado.gov/sites/default/files/2019a_1216_signed.pdf
NUR-550 Benchmark – Diverse Population Health Policy Analysis
Description:
Choose a current or proposed health-care policy aimed at providing equitable health-care services to a diverse population. Create a 12- to 15-slide PowerPoint presentation discussing the health care policy and how it improves access to quality, cost-effective health care for a specific population. Create 100-250 word speaker notes for each slide. Add extra slides for the title and references.
Include the following in your presentation:
- Describe the policy
- Discuss the diverse population that will be affected by this
- Explain how the policy is designed to improve cost-effectiveness and health care equity for the diverse
- Discuss why the policy is financially sound and explain how the policy incorporates the nursing perspective and relevant ethical, legal, and political Provide rationale to support your explanation.
- Describe what state, federal, global health policies, or goals the policy is related to and explain the degree to which each helps achieve equitable health care for the diverse
- Discuss advocacy strategies for improving access, quality, and cost-effective health care for the diverse population
- Discuss the professional and moral obligation of master’s prepared nurses to respect human dignity and advance the common good through working to promote health and prevent disease among diverse populations from a Christian
- You are required to cite eight peer-reviewed sources to complete this assignment. Sources must be published within the last 5 years and appropriate for the assignment criteria and nursing content.
- Refer to the resource, “Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations,” located in the Student Success Center, for additional guidance on completing this assignment in the appropriate style.
- While APA style is not required for the body of this NUR 550 assignment, solid academic writing is expected, and documentation of sources should be presented using APA formatting guidelines, which can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center.
- NUR 550 assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion.
- You are required to submit this Health Policy Analysis Essay NUR 550 assignment to LopesWrite. A link to the LopesWrite technical support articles is located in Class Resources if you need assistance.
Benchmark Information
This benchmark assignment assesses the following programmatic competencies:
MBA-MSN; MSN-Nursing Education; MSN Acute Care Nurse Practitioner-Adult-Gerontology; MSN Family Nurse Practitioner; MSN-Health Informatics; MSN-Health Care Quality and Patient Safety; MSN-Leadership in Health Care Systems; MSN-Public Health Nursing
- Examine financially sound health care policy that incorporates the nursing perspective and relevant ethical, legal, and political
- Determine advocacy strategies for improving access, quality, and cost-effective health care for diverse
- Integrate appropriate state, federal, and global health policies and goals into the design of equitable health care for
- Examine the professional and moral obligation of master’s-prepared nurses to respect human dignity and advance the common good through working to promote health and prevent disease among diverse populations from a Christian
READ MORE >>
Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional ObligationsBenchmark – Futu ...
Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional Obligations
Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional Obligations
Advanced registered nursing graduates are entering the profession at dynamic time when roles and scope of practice are shifting based on developments in legislation and policy in response to the evolving needs of the health care system Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional Obligations. Professional nursing organizations play an important role in making sure the perspectives of advanced registered nurses are heard, and in supporting nurse specialties in their efforts to expand their scope of practice and their full participation throughout the health care system.
For this assignment, you will conduct research on the current scope of practice for your specialty and efforts that are being made to expand that scope and the role of the advanced nurse in positively influencing the health care system. Write a 1,250-1,500-word paper that includes the following:
A discussion of the scope of your future role as an advanced registered nurse, including any regulatory, certification, or accreditation agencies that define that scope.
A discussion of three professional nursing organizations that you think are most influential in advancing the scope and influence of advanced nursing. Of these organizations, evaluate the one that you would most like to join. How do its goals and mission fit in with your worldview and philosophy of care? How might membership in this organization improve your practice? Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional Obligations
A discussion of a controversial or evolving issue that is most likely to affect your scope of practice or role in the next few years. How do you think this issue could influence the profession and other stakeholders, and why does it matters to the advanced registered nurse?
You are required to cite five to 10 sources to complete this assignment. Sources must be published within the last 5 years and appropriate for the assignment criteria and nursing content.
Prepare this assignment according to the guidelines found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center. An abstract is not required.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric prior to beginning the assignment to become familiar with the expectations for successful completion. Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional Obligations
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
My speciality is – Nurse Educator
I will upload the rubic for this project
Course CodeClass CodeAssignment TitleTotal PointsNUR-513NUR-513-O502250.0CriteriaPercentageUnsatisfactory (0.00%)Less than Satisfactory (80.00%)Satisfactory (88.00%)Good (92.00%)Excellent (100.00%)Content70.0%The Scope of Your Future Role as an Advanced Registered Nurse, Including Any Regulatory, Certification, or Accreditation Agencies That Define That Scope20.0%A discussion of the scope of the future role as an advanced registered nurse, including any regulatory, certification, or accreditation agencies that define that scope, is not included.A discussion of the scope of the future role as an advanced registered nurse, including any regulatory, certification, or accreditation agencies that define that scope, is present, but it lacks detail or is incomplete.A discussion of the scope of the future role as an advanced registered nurse, including any regulatory, certification, or accreditation agencies that define that scope, is present.A discussion of the scope of the future role as an advanced registered nurse, including any regulatory, certification, or accreditation agencies that define that scope, is clearly provided and well developed.A comprehensive discussion of the scope of the future role as an advanced registered nurse, including any regulatory, certification, or accreditation agencies that define that scope, is thoroughly developed with supporting details.Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional ObligationsThree Professional Nursing Organizations Identified as the Most Influential in Advancing the Scope and Influence of Advanced Nursing15.0%A discussion of three professional nursing organizations identified as the most influential in advancing the scope and influence of advanced nursing is not included.A discussion of three professional nursing organizations identified as the most influential in advancing the scope and influence of advanced nursing is present, but it lacks detail or is incomplete.A discussion of three professional nursing organizations identified as the most influential in advancing the scope and influence of advanced nursing is present.A discussion of three professional nursing organizations identified as the most influential in advancing the scope and influence of advanced nursing is clearly provided and well developed.A comprehensive discussion of three professional nursing organizations identified as the most influential in advancing the scope and influence of advanced nursing is thoroughly developed with supporting details.Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional ObligationsEvaluate the Professional Organization That Is Most Appealing, Including How Its Goals and Mission Fit in With Worldview, Philosophy of Care, and Ability to Improve Practice (5.3)15.0%An evaluation of the professional organization that is most appealing, including how its goals and mission fit in with worldview, philosophy of care, and ability to improve practice, is not included.An evaluation of the professional organization that is most appealing, including how its goals and mission fit in with worldview, philosophy of care, and ability to improve practice, is present, but it lacks detail or is incomplete.An evaluation of the professional organization that is most appealing, including how its goals and mission fit in with worldview, philosophy of care, and ability to improve practice, is present.An evaluation of the professional organization that is most appealing, including how its goals and mission fit in with worldview, philosophy of care, and ability to improve practice, is clearly provided and well developed.A comprehensive evaluation of the professional organization that is most appealing, including how its goals and mission fit in with worldview, philosophy of care, and ability to improve practice, is thoroughly developed with supporting details.A Controversial or Evolving Issue That Is Most Likely to Impact Scope of Practice or Role in the Next Few Years, Including How This Issue Could Influence the Profession and Other Stakeholders and Why It Matters to the Advanced Registered Nurse15.0%A discussion of a controversial or evolving issue that is most likely to impact scope of practice or role in the next few years, including how this issue could influence the profession and other stakeholders and why it matters to the advanced registered nurse, is not included.A discussion of a controversial or evolving issue that is most likely to impact scope of practice or role in the next few years, including how this issue could influence the profession and other stakeholders and why it matters to the advanced registered nurse, is present, but it lacks detail or is incomplete.A discussion of a controversial or evolving issue that is most likely to impact scope of practice or role in the next few years, including how this issue could influence the profession and other stakeholders and why it matters to the advanced registered nurse, is present.A discussion of a controversial or evolving issue that is most likely to impact scope of practice or role in the next few years, including how this issue could influence the profession and other stakeholders and why it matters to the advanced registered nurse, is clearly provided and well developed.A comprehensive discussion of a controversial or evolving issue that is most likely to impact scope of practice or role in the next few years, including how this issue could influence the profession and other stakeholders and why it matters to the advanced registered nurse, is thoroughly developed with supporting details.Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional ObligationsRequired Sources5.0%Sources are not included.Number of required sources is only partially met.Number of required sources is met, but sources are outdated or inappropriate.Number of required sources is met. Sources are current, but not all sources are appropriate for the assignment criteria and nursing content.Number of required resources is met. Sources are current, and appropriate for the assignment criteria and nursing content.Organization and Effectiveness20.0%Thesis Development and Purpose7.0%Paper lacks any discernible overall purpose or organizing claim.Thesis is insufficiently developed or vague. Purpose is not clear.Thesis is apparent and appropriate to purpose.Thesis is clear and forecasts the development of the paper. Thesis is descriptive and reflective of the arguments and appropriate to the purpose.Thesis is comprehensive and contains the essence of the paper. Thesis statement makes the purpose of the paper clear.Argument Logic and Construction8.0%Statement of purpose is not justified by the conclusion. The conclusion does not support the claim made. Argument is incoherent and uses noncredible sources.Sufficient justification of claims is lacking. Argument lacks consistent unity. There are obvious flaws in the logic. Some sources have questionable credibility.Argument is orderly, but may have a few inconsistencies. The argument presents minimal justification of claims. Argument logically, but not thoroughly, supports the purpose. Sources used are credible. Introduction and conclusion bracket the thesis.Argument shows logical progressions. Techniques of argumentation are evident. There is a smooth progression of claims from introduction to conclusion. Most sources are authoritative.Clear and convincing argument that presents a persuasive claim in a distinctive and compelling manner. All sources are authoritative.Mechanics of Writing (includes spelling, punctuation, grammar, language use)5.0%Surface errors are pervasive enough that they impede communication of meaning. Inappropriate word choice or sentence construction is used.Frequent and repetitive mechanical errors distract the reader. Inconsistencies in language choice (register) or word choice are present. Sentence structure is correct but not varied.Some mechanical errors or typos are present, but they are not overly distracting to the reader. Correct and varied sentence structure and audience-appropriate language are employed.Prose is largely free of mechanical errors, although a few may be present. The writer uses a variety of effective sentence structures and figures of speech.Writer is clearly in command of standard, written, academic English.Format10.0%Paper Format (Use of appropriate style for the major and assignment)5.0%Template is not used appropriately or documentation format is rarely followed correctly.Template is used, but some elements are missing or mistaken; lack of control with formatting is apparent.Template is used, and formatting is correct, although some minor errors may be present.Template is fully used; There are virtually no errors in formatting style.All format elements are correct.Documentation of Sources (citations, footnotes, references, bibliography, etc., as appropriate to assignment and style)5.0%Sources are not documented.Documentation of sources is inconsistent or incorrect, as appropriate to assignment and style, with numerous formatting errors.Sources are documented, as appropriate to assignment and style, although some formatting errors may be present.Sources are documented, as appropriate to assignment and style, and format is mostly correct.Sources are completely and correctly documented, as appropriate to assignment and style, and format is free of error.Benchmark – Future Scope, Role, and Professional ObligationsTotal Weightage100%READ MORE >>
Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms PaperBenchmark PSY 402 Memory and ...
Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms Paper
Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms Paper
This paper aims to understand how the brain and memory processes are intertwined and how certain techniques can improve these processes. In an essay of 1,000-1,250 words, discuss how memories are formed and maintained in the brain through the actions of neural circuitry.

Use at least four scholarly resources to address the following questions:
- Theoretically, how is working memory similar to and different from long-term memory?
- How are memories formed in the brain (using neural circuitry), and how are they maintained?
- When is it adaptive to remember, and in what ways may it be adaptive to forget?
- Given what we know about brain mechanisms in memory, are our memories accurate? Explain your answer using information on how memories are stored in the brain.
- How can knowledge of the brain and memory systems help individuals suffering from memory problems (e.g., poor memory, amnesia, PTSD)?
- Compare age and environment’s role in how memories are formed and maintained.
CLICK HERE TO ORDER Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms Paper
Prepare this assignment according to the guidelines in the APA Style Guide in the Student Success Center. An abstract is not required.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric before beginning the assignment to familiarize yourself with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
This benchmark assignment assesses the following programmatic competency: 1.3: Compare biological and psychological explanations of the brain and its functions, and 2.3: Apply critical thinking skills in solving problems related to behavior and mental processes.
Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms Paper Benchmark Article Review
Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms Paper Details:
For this assignment, select a peer-reviewed journal article reaboutroblem-solving, decision-making, or an intelligence theory discussed in class (e.g., fluid or crystalline intelligence, primary/secondary reinforcers, biases, or effective problem-solving strategies).
The article must meet the following criteria:
- The article must be from a peer-reviewed journal.
- The article must be obtained from the GCU Library.
- The article must be a research study rather than a literature review (i.e., the article has to have methods, results, and discussion sections).
- The article must utilize a cognitive or behavioral theory, model, or effect.
- This article review aims to get you to think critically about an area of cognition or learning. After reading your chosen article, address the following questions. Use subheadings to differentiate between the various aspects of your review. Remember, APA guidelines can be found in the APA Style Guide, located in the Student Success Center.
Benchmark PSY 402 Memory and Brain Mechanisms Paper Major Findings/Conclusions:
- Be sure to include the major findings of the study.
- What conclusions did the researchers draw from the data?
Implications for the Field of Psychology (how the findings could be used/applied in the field):
- Include how the study results can be applied (e.g., why are the study findings important?). These may be the implications the authors put forth or your ideas (be sure to cite if they are not).
- How would psychology/education/counseling professionals benefit (learn) from the findings?
- How might the results improve knowledge or application in the field? What should psychology professionals “take away” from the findings?
Method/Participants:
- Describe the basics of how the study was conducted. What procedures were used?
- Who were the participants?
Strengths/Limitations of the Study:
- Include at least one strength AND one limitation you saw in the study.
- Explain why you believe each is a strength or limitation. Hint: study findings are not “strengths” in and of themselves.
The article review should be 1,000-1,250 words. Include a minimum of three scholarly articles.
Prepare this assignment according to the guidelines in the APA Style Guide in the Student Success Center. An abstract is not required.
This assignment uses a rubric. Please review the rubric before beginning the assignment to familiarize yourself with the expectations for successful completion.
You are required to submit this assignment to LopesWrite. Please refer to the directions in the Student Success Center.
This benchmark assignment assesses the following programmatic competency: 4.4: Explain the importance of maintaining knowledge of current trends in psychology.
READ MORE >>
