NURS 6630 Week 2 Discussion Foundational NeuroscienceAgonist-to-antagonist Spectrum of Psychopharmac
NURS 6630 Week 2 Discussion Foundational Neuroscience
Agonist-to-antagonist Spectrum of Psychopharmacologic Agents
A medicine or substance that binds to and activates a specific receptor to create a desired biological response is known as an agonist. Exogenous agonists are substances that imitate the activities of endogenous agonists. Endogenous agonists are those created within the body, whereas exogenous agonists are those synthesized outside of the body. Agonists are divided into three types based on their intrinsic efficacy: full agonists, partial agonists, and inverse agonists.
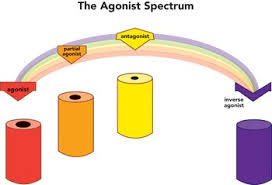
A complete agonist has a high intrinsic effectiveness, which means it activates all receptors to their maximum potential, resulting in the maximum expected response. A partial agonist has a lower intrinsic efficacy than a full agonist, which results in sub-maximal receptor activation and a reduced physiological response. Despite binding to the same receptor location as the agonist, an inverse agonist has a negative intrinsic effectiveness because it causes a physiological response that is antagonistic or opposite to the agonist (Berg & Clarke, 2018). An antagonist, unlike an agonist, has no intrinsic efficacy but has a high affinity for receptors and inhibits the effects of agonists. Depending on the drug’s intrinsic activity and affinity, the agonist-to-antagonist spectrum has consequences for the choice of psychopharmacological drugs.
Comparison Of G Couple Proteins And Ion Gated Channels
G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs and ion gated channels (IGCs) are receptors that are usually activated by stimuli to mediate cellular responses. GPRCs are more numerous than IGCs and function through second messenger networks. The activation of these receptors by ligands enables them to bind to G-proteins, which promote the exchange of GTP for GDP, resulting in a cascade of activities that induce a cellular response (Weis et al., 2018). IGCs are transmembrane proteins with a central pore that opens and closes to regulate ion flow across cell membranes (Phillips et al., 2020). Due to the coupling, GPCRs respond to signals more slowly and are activated by slower neurotransmitters like serotonin. Faster neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, activate IGCs, resulting in a faster response.
Role Of Epigenetics In Pharmacologic Action
Epigenetics is increasingly being adopted in the development of therapeutic pharmacological agents. In epigenetics, DNA methylation or histone modification regulate DNA transcription without inflicting any changes to the DNA sequence (Kringel et al., 2021). Through conformational changes in transcription factors, this results in enhanced or decreased transcription of the target genes or exposure of desired regions of the DNA. As a result, drugs targeting specific genes that contribute to the genesis of numerous diseases, including psychiatric illnesses, can be produced. However, the efficacy of these therapeutic epigenetic pharmacologic agents, as well as expected responses, may be dependent on the existence or modification of the target genes among individuals; so, diversity is to be expected.
Impact of the Above Information on Prescription of Medications to Patients
Given the foregoing, it is critical to understand an individual’s genetic background prior to treatment. This is due to the fact that some genes are heritable, which is most typically seen in the medical environment as a positive family history of a particular sickness. As a result, obtaining a complete medical and family history before to treatment is critical. In the case of multiple therapy failures, genetic testing should be considered. Epigenetics is influenced by genetic and environmental variables; thus, medical professionals must be aware of this. Similar conditions in twins, for example, may not respond to treatment in the same way, necessitating the need to tailor care.
NURS 6630 Week 2 Discussion Foundational Neuroscience References
Berg, K., & Clarke, W. (2018). Making Sense of Pharmacology: Inverse Agonism and Functional Selectivity. International Journal Of Neuropsychopharmacology, 21(10), 962-977. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyy071
Kringel, D., Malkusch, S., & Lötsch, J. (2021). Drugs and Epigenetic Molecular Functions. A Pharmacological Data Scientometric Analysis. International Journal Of Molecular Sciences, 22(14), 7250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147250
Phillips, M., Nigam, A., & Johnson, J. (2020). The interplay between Gating and Block of Ligand-Gated Ion Channels. Brain Sciences, 10(12), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10120928
Weis, W. I., & Kobilka, B. K. (2018). The Molecular Basis of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Activation. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 87, 897–919. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-060614-033910
Also read:
NURS 6630 Week 9 A Young Girl With ADHD
NURS 6630 Week 2 Explain the Agonist-to-Antagonist Spectrum of Action of Psychopharmacologic Agents
NURS 6630 WEEK 1 ASSIGNMENT 2 – SHORT ANSWER ASSESSMENT
As a psychiatric and mental health nurse practitioner, before you can recommend potential pharmacotherapeutics to address a patient’s condition or disorder, you must understand the basic function and structure of the neuron and central nervous system. For this Assignment, you will review and apply your understanding of neuroanatomy by addressing a set of short answer prompts.
To Prepare:
Review the Learning Resources for this week in preparation to complete this Assignment.
Reflect on the basic function and structure of the neuron in relation to the central nervous system.
Reflect on the inter-connectedness between neurons and the central nervous system, including the pathway and distribution of electrical impulses.
Reflect on how neurons communicate with each other and review the concept of neuroplasticity.
TO COMPLETE:
Address the following Short Answer prompts for your Assignment. Be sure to include references to the Learning Resources for this week.
In 4 or 5 sentences, describe the anatomy of the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron. Include each part of the neuron and a general overview of electrical impulse conduction, the pathway it travels, and the net result at the termination of the impulse. Be specific and provide examples.
Answer the following (listing is acceptable for these questions):
What are the major components that make up the subcortical structures?
Which component plays a role in learning, memory, and addiction?
What are the two key neurotransmitters located in the nigra striatal region of the brain that play a major role in motor control?
In 3 or 4 sentences, explain how glia cells function in the central nervous system. Be specific and provide examples.
The synapse is an area between two neurons that allows for chemical communication. In 3 or 4 sentences, explain what part of the neurons are communicating with each other and in which direction does this communication occur? Be specific.
In 3–5 sentences, explain the concept of “neuroplasticity.” Be specific and provide examples.
RESOURCES
Be sure to review the Learning Resources before completing this activity.
Click the weekly resources link to access the resources.
WEEKLY RESOURCES
BY DAY 7
Submit your Assignment.
SUBMISSION INFORMATION
Before submitting your final assignment, you can check your draft for authenticity. To check your draft, access the Turnitin Drafts from the Start Here area.
To submit your completed assignment, save your Assignment as WK1Assgn2_LastName_Firstinitial
Then, click on Start Assignment near the top of the page.
Next, click on Upload File and select Submit Assignment for review.
LEARNING RESOURCES
Required Readings (MUST BE CITED)
Stahl, S. M. (2021). Stahl’s essential psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical applications (5th Ed.) Cambridge University Press.
Chapter 1, “Chemical Neurotransmission” (pp. 1-28)
Required Media
Psychopharmacologic Approaches to Treatment of Psychopathology (3m)
Mental Health TV. (2022, Oct 7). Psychopharmacology-Module one. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ku8PZlXAYco
Mental Health TV. (2022, Oct 7). Psychopharmacology-Module two. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jw9uc4qVqew
Mental Health TV. (2022, Oct 7). Psychopharmacology-Module three. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xLGfB3E4rqE&t=538s
Optional Media
Pathopharmacology: Disorders of the Nervous System: Exploring the Human Brain
Dr. Norbert Myslinski reviews the structure and function of the human brain. Using human brains, he examines and illustrates the development of the brain and areas impacted by disorders associated with the brain. (15m)
Introduction to Advanced Pharmacology
In this media presentation, Dr. Terry Buttaro, associate professor of practice at Simmons School of Nursing and Health Sciences, discusses the importance of pharmacology for the advanced practice nurse. (6m)
Rubric – NURS_6630_Week1_Assignment_Rubric
NURS_6630_Week1_Assignment_Rubric
Criteria
Ratings
Pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeIn 4 or 5 sentences, describe the anatomy of the basic unit of the nervous system, the neuron. Include each part of the neuron and a general overview of electrical impulse conduction, the pathway it travels, and the net result at the termination of the impulse. Be specific and provide examples.
13 to >11.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
The response accurately and clearly describes in detail the anatomy of the neuron. The response accurately and clearly describes in detail each part of the neuron, and it includes a detailed explanation of the general overview of electrical impulse conduction, the pathway it travels, and the net result at the termination of the impulse…. Examples fully support the response provided.
11 to >10.0 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
The response accurately describes the anatomy of the neuron. The response accurately describes each part of the neuron, and it includes a general overview of electrical impulse conduction, the pathway it travels, and the net result at the termination of the impulse…. Examples support the response provided.
10 to >9.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
The response provides an inaccurate or vague description of the anatomy of the neuron. The response inaccurately or vaguely describes each part of the neuron, and it includes an inaccurate or vague overview of electrical impulse conduction, the pathway it travels, and the net result at the termination of the impulse…. Examples vaguely support the response provided.
9 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
The response provides an inaccurate or incomplete description of the anatomy of the neuron, or is missing. The response inaccurately or incompletely describes each part of the neuron, and it includes an inaccurate or vague overview of electrical impulse conduction, the pathway it travels, and the net result at the termination of the impulse, or is missing…. Examples do not support the response provided, or is missing.
13 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeAnswer the following (listing is acceptable for these questions):a. What are the major components that make up the subcortical structures?b. Which component plays a role in learning, memory, and addiction?c. What are the two key neurotransmitters located in the nigra striatal region of the brain that play a major role in motor control?
13 to >11.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
The response accurately and clearly details the major components that make up the subcortical structures…. The response accurately and clearly details which component plays a role in learning, memory, and addiction…. The response accurately and clearly identifies the two neurotransmitters located in the nigra striatal region of the brain that play a major role in motor control.
11 to >10.0 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
The response accurately identifies the major components that make up the subcortical structures…. The response accurately identifies which component plays a role in learning, memory, and addiction…. The response accurately identifies the two neurotransmitters located in the nigra striatal region of the brain that play a major role in motor control.
10 to >9.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
The response inaccurately identifies the major components that make up the subcortical structures…. The response inaccurately identifies which component plays a role in learning, memory, and addiction…. The response inaccurately identifies two neurotransmitters located in the nigra striatal region of the brain that play a major role in motor control.
9 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
The response inaccurately and incompletely identifies the major components that make up the subcortical structures, or is missing…. The response inaccurately and incompletely identifies which component plays a role in learning, memory, and addiction, or is missing…. The response inaccurately and incompletely identifies two neurotransmitters in the nigra striatal region of the brain that play a major role in motor control, or is missing.
13 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeIn 3 or 4 sentences, explain how glia cells function in the central nervous system. Be specific and provide examples.
13 to >11.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
The response accurately and clearly explains in detail how glia cells function in the central nervous system…. Examples fully support the response provided.
11 to >10.0 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
The response accurately explains how glia cells function in the central nervous system…. Examples support the response provided.
10 to >9.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
The response inaccurately or vaguely explains how glia cells function in the central nervous system…. Examples inaccurately or vaguely support the response provided.
9 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
The response inaccurately and vaguely explains how glia cells function in the central nervous system, or is missing…. Examples do not support the response provided, or is missing.
13 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeThe synapse is an area between two neurons that allows for chemical communication. In 3 or 4 sentences, explain what part of the neurons are communicating with each other and in which direction does this communication occur? Be specific.
13 to >11.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
The response accurately and clearly explains in detail the part of the neurons that communicate with each other and the direction in which this communication occurs.
11 to >10.0 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
The response accurately explains the part of the neurons that communicate with each other and the direction in which this communication occurs.
10 to >9.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
The response inaccurately or vaguely explains the part of the neurons that communicate with each other and the direction in which this communication occurs.
9 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
The response inaccurately and vaguely explains the part of the neurons that communicate with each other and the direction in which this communication occurs, or is missing.
13 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeIn 3–5 sentences, explain the concept of “neuroplasticity.” Be specific and provide examples.
13 to >11.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
The response accurately and clearly explains in detail the concept of neuroplasticity…. Examples provided fully support the response provided.
11 to >10.0 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
The response accurately explains the concept of neuroplasticity…. Examples provided support the response provided.
10 to >9.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
The response inaccurately or vaguely explains the concept of neuroplasticity…. Examples inaccurately or vaguely support the response provided.
9 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
The response inaccurately and vaguely explains the concept of neuroplasticity, or is missing…. Examples do not support the response provided, or is missing.
13 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeWritten Expression and Formatting – English writing standards: Correct grammar, mechanics, and proper punctuation
5 to >4.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
Uses correct grammar, spelling, and punctuation with no errors.
4 to >3.5 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
Contains a few (1 or 2) grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
3.5 to >2.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
Contains several (3 or 4) grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
2 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
Contains many (? 5) grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors that interfere with the reader’s understanding.
5 pts
This criterion is linked to a Learning OutcomeWritten Expression and Formatting – The paper follows correct APA format for title page, headings, font, spacing, margins, indentations, page numbers, parenthetical/in-text citations, and reference list.
5 to >4.0 pts
Excellent Point range: 90–100
Uses correct APA format with no errors.
4 to >3.5 pts
Good Point range: 80–89
Contains a few (1 or 2) APA format errors.
3.5 to >2.0 pts
Fair Point range: 70–79
Contains several (3 or 4) APA format errors.
2 to >0 pts
Poor Point range: 0–69
Contains many (? 5) APA format errors.
5 pts
Total Points: 75
NURS 6630 Week 2 Discussion Foundational Neuroscience
As a psychiatric and mental health nurse practitioner, it is essential for you to have a strong background in foundational neuroscience. In order to diagnose and treat patients, you must not only understand the pathophysiology of psychiatric disorders but also how medications for these disorders impact the central nervous system. These concepts of foundational neuroscience can be challenging to understand. Therefore, this Discussion is designed to encourage you to think through these concepts, develop a rationale for your thinking, and deepen your understanding by interacting with your colleagues.
For this Discussion, review the Learning Resources and reflect on the concepts of foundational neuroscience as they might apply to your role as the psychiatric mental health nurse practitioner in prescribing medications for patients
BY DAY 3 OF WEEK 2
Post a response to each of the following:
- Explain the agonist-to-antagonist spectrum of action of psychopharmacologic agents, including how partial and inverse agonist functionality may impact the efficacy of psychopharmacologic treatments.
- Compare and contrast the actions of g couple proteins and ion gated channels.
- Explain how the role of epigenetics may contribute to pharmacologic action.
- Explain how this information may impact the way you prescribe medications to patients. Include a specific example of a situation or case with a patient in which the psychiatric mental health nurse practitioner must be aware of the medication’s action.
Upload a copy of your discussion writing to the draft Turnitin for plagiarism check. Your faculty holds the academic freedom to not accept your work and grade at a zero if your work is not uploaded as a draft submission to Turnitin as instructed.
Read a selection of your colleagues’ responses.
BY DAY 6 OF WEEK 2
Respond to at least two of your colleagues on two different days in one of the following ways:
- If your colleagues’ posts influenced your understanding of these concepts, be sure to share how and why. Include additional insights you gained.
- If you think your colleagues might have misunderstood these concepts, offer your alternative perspective and be sure to provide an explanation for them. Include resources to support your perspective.
Note: For this Discussion, you are required to complete your initial post before you will be able to view and respond to your colleagues’ postings. Begin by clicking on the Reply button to complete your initial post. Remember, once you click on Post Reply, you cannot delete or edit your own posts and you cannot post anonymously. Please check your post carefully before clicking on Post Reply!
LEARNING RESOURCES
Required Readings
- Stahl, S. M. (2021). Stahl’s essential psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific basis and practical applications (5th Ed.) Cambridge University Press.
- Chapter 2, “Transporters, Receptors, and Enzymes as Targets of Psychopharmacological Drug Action” (pp. 29-50)
- Chapter 3, “Ion Channels as Targets of Psychopharmacological Drug Action) (pp. 51-76)
Required Media
- The University of British Columbia. (n. d.). Neuroanatomy videosLinks to an external site.. http://neuroanatomy.ca/videos.html
Note: Please review all of the media under the neuroanatomy series.
- Mental Health TV. (2022, Oct 7). Psychopharmacology-Module fourLinks to an external site. [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=46Ioy6SSta4&t=89s
- Mental Health TV. (2022, Oct 7). Psychopharmacology-Module five [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1ynTQB59KW0&t=16s
Optional Resources
- Pathopharmacology: Disorders of the Nervous System: Exploring the Human Brain
- Introduction to Advanced Pharmacology
Dr. Norbert Myslinski reviews the structure and function of the human brain. Using human brains, he examines and illustrates the development of the brain and areas impacted by disorders associated with the brain. (15m)
In this media presentation, Dr. Terry Buttaro, associate professor of practice at Simmons School of Nursing and Health Sciences, discusses the importance of pharmacology for the advanced practice nurse. (6m)
NURS 6630 Week 3: Concepts in Assessing Medication Adherence and Strategies To Mitigate Non-Adherence
Self Assessment QUIZ
Question 1 0 pts
Introducing adherence in facilitating treatment goals is something that would be necessary in a patient who has previously displayed nonadherence patterns.
Group of answer choices
True
False
Question 2 0 pts
G-protein coupled receptors are targets for several psychiatric medications. Given what we know about these receptors, what is the ultimate result we will see when one of them is activated in a way that would potentiate an action?
Group of answer choices
A. Intracellular activation of second messengers
B. Protein phosphorylation
C. Modification of gene expression
Question 3 0 pts
Which neurotransmitter is considered the major excitatory neurotransmitter?
Group of answer choices
A. Glycine
B. GABA
C. Glutamate
D. Serotonin
Question 4 0 pts
G-protein coupled receptors are examples of what type of effector pathway?
Group of answer choices
A. Slow effector pathways
B. Rapid effector pathways
C. NMDA glutamate receptor pathways
D. Modulated effector pathways
Question 5 0 pts
Of the components of patient-focused interventions to enhance adherence, which component includes the following strategies: adaptive thinking, use of cues, and support?
Group of answer choices
Motivation
Skills
Logistics
Education
Question 6 0 pts
Motivation is a component of patient-focused interventions to enhance adherence. Based on the transtheoretical model, readiness to change can fluctuate across five stages. Which stage is represented by the patient who is aware that a problem exists and, while seriously thinking about overcoming it, has not yet committed to a plan of action?
Group of answer choices
Preparation
Action
Contemplation
Maintenance
Question 7 0 pts
The human brain is subcategorized into four major structures. These structures include the cerebral cortex, brainstem, subcortical structures, and the cerebellum. Of these major categories, which one houses the area of the brain that has been found in some neuropathological studies of patients with schizophrenia to be of smaller size?
Group of answer choices
Cerebral cortex
Brainstem
Subcortical structures
Cerebellum
Question 8 0 pts
Neurotransmitters are defined by four essential characteristics. These are:
Group of answer choices
A. Neurotransmitters are synthesized within presynaptic neurons.
B. Depolarization of a neuron results in the release of a neurotransmitter, which exerts a multitude of actions on the postsynaptic neuron.
C. Their action on postsynaptic neurons can be replicated by administering a drug that mimics the activity of the endogenous neurotransmitter.
D. Their action in the synaptic cleft is terminated by a specific action.
E. A, C, and D only
Question 9 0 pts
Serotonin (5HT) is a neurotransmitter associated with mood, sleep, and psychosis. There are several serotonin receptors all over the human body. A unique aspect of the second generation antipsychotics is their ability to block 5HT2a receptors. What is the effect of this inhibition?
Group of answer choices
A. Stabilizes dopamine concentrations in the CNS
B. Induces anxiety
C. Causes hallucinations
D. Reduces platelet function
Question 10 0 pts
Treatment adherence is affected by several different factors. Clinical factors include mood, anxiety, psychosis, and substance misuse. There are also patient factors such as knowledge, attitude, and beliefs; economic and racial/ethnic disparities, and clinical encounters. A patient who presents hopeless, with decreased energy, and poor concentration is affected by which factor?
Group of answer choices
Substance misuse
Knowledge deficits
Attitude ad belief system
Mood
Question 11 0 pts
A patient arrives in the ED via EMS having a grand mal seizure. The ED physician instructs the RN to give 10 milligrams of Diazepam IV X1 dose STAT. The patient’s seizure breaks within 2 minutes of the Diazepam being administered. The mechanism by which this medication causes rapid resolution of seizure activity is via which receptor type (effector pathway/receptor subtype)?
Group of answer choices
A. Slow effector pathways/G-protein coupled receptor
B. Slow effector pathway/ion channel
C. Rapid effector pathways/G-protein coupled receptor
D. Rapid effector pathway/ion channel
Question 12 0 pts
Neurotransmission is unidirectional insofar as chemical and electrical conduction is concerned within the individual neuron. Of the following descriptions, which best characterizes the order of neurotransmitter/receptor interaction that results in an electrical signal impulse and the release of another neurotransmitter for interaction in the synaptic cleft (signal conduction through a neuron)?
Group of answer choices
Cell body, dendrites, Axon, Axon terminals
Dendrites, Axon, Cell body, Axon, Axon terminals
Dendrites, Cell body, Axon, Axon terminals
Axon terminals, Axon, Cell body, Dendrites
Question 15 0 pts
If a patient admits to taking his medication every other day (instead of daily, as prescribed), a potential concern would be:
Group of answer choices
A. Sufficient understanding or acceptance of the illness
B. Abuse of the medication
C. Expense
D. Is the desired effect recognized at a lower daily dose?
Question 16 0 pts
Receptors trigger one of two effector pathways resulting in changes in neuronal activity. These changes will, ultimately, effect gene expression. Which effector pathway is characterized by ion flux through transmitter-activated channels resulting in an altered membrane potential and neuronal activity?
Group of answer choices
A. Slow effector pathways
B. Modulated effector pathways
C. Rapid effector pathways
D. NMDA glutamate receptor pathways
Question 17 0 pts
Upon blocking a Serotonin reuptake pump, what happens in the synaptic cleft and on the post synaptic cell membrane?
Group of answer choices
A. The result will be an increase in available Serotonin in the synaptic cleft causing the post synaptic cell to increase the number of Serotonin receptors.
B. The result will be an increase in the available Serotonin in the synaptic cleft causing the post synaptic neuron to reduce the number
Solution:
It's easy, but reach out anytime if you encounter any difficulties at any point.
WhatsApp boutessays@gmail.com
NEED A UNIQUE PAPER ON THE ABOVE DETAILS?
Order Now
GET HELP INSTANTLY
Place your order to get best research help
